Systematic literature review of burden of illness in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP)
- PMID: 32583051
- PMCID: PMC8463372
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-020-09998-8
Systematic literature review of burden of illness in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP)
Abstract
Background: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a rare neurological disorder characterised by muscle weakness and impaired sensory function. The present study provides a comprehensive literature review of the burden of illness of CIDP.
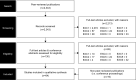
Methods: Systematic literature search of PubMed, Embase, and key conferences in May 2019. Search terms identified studies on the epidemiology, humanistic burden, current treatment, and economic burden of CIDP published since 2009 in English.
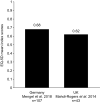
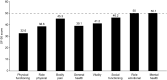
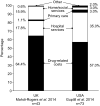
Results: Forty-five full texts and nineteen conference proceedings were identified on the epidemiology (n = 9), humanistic burden (n = 7), current treatment (n = 40), and economic burden (n = 8) of CIDP. Epidemiological studies showed incidence and prevalence of 0.2-1.6 and 0.8-8.9 per 100,000, respectively, depending on geography and diagnostic criteria. Humanistic burden studies revealed that patients experienced physical and psychosocial burden, including impaired physical function, pain and depression. Publications on current treatments reported on six main types of therapy: intravenous immunoglobulins, subcutaneous immunoglobulins, corticosteroids, plasma exchange, immunosuppressants, and immunomodulators. Treatments may be burdensome, due to adverse events and reduced independence caused by treatment administration setting. In Germany, UK, France, and the US, CIDP economic burden was driven by direct costs of treatment and hospitalisation. CIDP was associated with indirect costs driven by impaired productivity.
Conclusions: This first systematic review of CIDP burden of illness demonstrates the high physical and psychosocial burden of this rare disease. Future research is required to fully characterise the burden of CIDP, and to understand how appropriate treatment can mitigate burden for patients and healthcare systems.
Keywords: Burden; CIDP; Cost; Epidemiology; QoL; Treatment.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
LQ has provided expert testimony for Grifols, Sanofi-Genzyme, Novartis, UCB, Roche, and CSL Behring, and received research funds from Novartis Spain, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Grifols. MC, EP, and SA are, or were, employees of Huron Consulting Group. Huron Consulting Group received funding from CSL Behring GmbH to perform the study. IV and PS are, or were, employees of CSL Behring GmbH. MH is an employee of Optimal Access Life Science Consulting Limited and received funding from CSL Behring.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

