Immunoinformatics study to search epitopes of spike glycoprotein from SARS-CoV-2 as potential vaccine
- PMID: 32583729
- PMCID: PMC7332869
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1780944
Immunoinformatics study to search epitopes of spike glycoprotein from SARS-CoV-2 as potential vaccine
Abstract
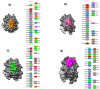
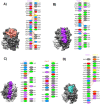
The Coronavirus disease named COVID-19 is caused by the virus reported in 2019 first identified in China. The cases of this disease have increased and as of June 1st, 2020 there are more than 216 countries affected. Pharmacological treatments have been proposed based on the resemblance of the HIV virus. With regard to prevention there is no vaccine, thus, we proposed to explore the spike protein due to its presence on the viral surface, and it also contains the putative viral entry receptor as well as the fusion peptide (important in the genome release). In this work we have employed In Silico techniques such as immunoinformatics tools which permit the identification of potential immunogenic regions on the viral surface (spike glycoprotein). From these analyses, we identified four epitopes E332-370, E627-651, E440-464 and E694-715 that accomplish essential features such as promiscuity, conservation grade, exposure and universality, and they also form stable complexes with MHCII molecule. We suggest that these epitopes could generate a specific immune response, and thus, they could be used for future applications such as the design of new epitope vaccines against the SARS-CoV-2.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: Epitope; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; spike glycoprotein; vaccine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A vaccine built from potential immunogenic pieces derived from the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein: A computational approximation.J Immunol Methods. 2022 Mar;502:113216. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113216. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Immunol Methods. 2022. PMID: 35007561 Free PMC article.
-
A rational design of a multi-epitope vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 which accounts for the glycan shield of the spike glycoprotein.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Sep;40(15):7099-7113. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1894986. Epub 2021 Mar 10. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33715598 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics prediction of overlapping CD8+ T-cell, IFN-γ and IL-4 inducer CD4+ T-cell and linear B-cell epitopes based vaccines against COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2).Vaccine. 2021 Feb 12;39(7):1111-1121. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.01.003. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Vaccine. 2021. PMID: 33478794 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of B-Cell Epitopes for Eliciting Neutralizing Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein through Bioinformatics and Monoclonal Antibody Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 14;23(8):4341. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084341. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunoinformatics Approach for the Identification and Characterization of T Cell and B Cell Epitopes towards the Peptide-Based Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2.Arch Med Res. 2021 May;52(4):362-370. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Arch Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33546870 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Up State of the SARS-COV-2 Spike Homotrimer Favors an Increased Virulence for New Variants.Front Med Technol. 2021 Jun 30;3:694347. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2021.694347. eCollection 2021. Front Med Technol. 2021. PMID: 35047936 Free PMC article.
-
The Advantage of Using Immunoinformatic Tools on Vaccine Design and Development for Coronavirus.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;10(11):1844. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111844. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36366353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two MP2CL5 Antigen Vaccines from Naegleria fowleri Stimulate the Immune Response against Meningitis in the BALB/c Model.Infect Immun. 2023 Jul 18;91(7):e0018123. doi: 10.1128/iai.00181-23. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 37272791 Free PMC article.
-
Designing multi-epitope based peptide vaccine targeting spike protein SARS-CoV-2 B1.1.529 (Omicron) variant using computational approaches.Struct Chem. 2022;33(6):2243-2260. doi: 10.1007/s11224-022-02027-6. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Struct Chem. 2022. PMID: 36160688 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics-guided designing and in silico analysis of epitope-based polyvalent vaccines against multiple strains of human coronavirus (HCoV).Expert Rev Vaccines. 2022 Dec;21(12):1851-1871. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2021.1874925. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 33435759 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
