Anxiety as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of depression: a prospective examination of community-dwelling men (the MrOS study)
- PMID: 32584189
- PMCID: PMC7759580
- DOI: 10.1080/08870446.2020.1779273
Anxiety as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of depression: a prospective examination of community-dwelling men (the MrOS study)
Abstract
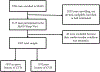
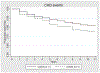
Anxiety and depression have been linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Whether anxiety is a risk factor independent from depression, and if associations are limited to specific CVD outcomes remains unclear. Design: Participants (N = 3135) of the prospective Osteoporotic Fracturs in Men Sleep ancillary study were community-dwelling men (age ≥ 65) living in the US. Main outcome measures: The Goldberg Anxiety and Depression Scales, coronary heart disease (CHD) and cerebrovascular disease (CER). We used Cox proportional hazards models to calculate adjusted hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals. Results: During 12 years of follow-up, we accrued 612 cases of CHD and 291 cases of CER (incident or repeat-event). Overall, we observed no association between anxiety or depression and CER. Anxiety was significantly associated with CHD, but this effect was attenuated after controlling for depression and covariates. Depression was significantly associated with CHD after similar adjustments. For men without prior history of CVD, neither anxiety nor depression were associated with incident CHD. Conclusions: Anxiety was not a significant independent predictor of CHD or CER, suggesting that previous findings of anxiety as a risk factor of CVD might be attributed to failure to control for the effect of depression.
Keywords: Anxiety; cardiovascular disease; coronary heart disease; depression; elderly; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
Dr Stone reports grants from NIH, during the conduct of the study. The other authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarenga ME, & Byrne D (2016). Anxiety and Cardiovascular Disease: Epidemiology and Proposed Mechanisms In Alvarenga ME & Byrne D (Eds.), Handbook of Psychocardiology (pp. 247–263). Springer; Singapore: 10.1007/978-981-287-206-7_10 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL070848/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071194/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070847/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000128/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042145/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042168/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070841/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR066160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070838/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070837/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042143/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States