EUS-guided pancreatic drainage: A steep learning curve
- PMID: 32584312
- PMCID: PMC7430898
- DOI: 10.4103/eus.eus_3_20
EUS-guided pancreatic drainage: A steep learning curve
Abstract
Background and objective: EUS-guided pancreatic drainage (EUS-PD) is an efficacious, acceptable risk option for patients with pancreatic duct obstruction who fail conventional ERCP. The aim of this study was to define the learning curve (LC) for EUS-PD.
Methods: Consecutive patients undergoing EUS-PD by a single operator were included from a dedicated registry. Demographics, procedural info, adverse events, and follow-up data were collected. Nonlinear regression and cumulative sum (CUSUM) analyses were conducted for the LC.
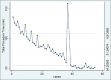
Results: Fifty-six patients were included (54% of male, with a mean age of 58 years). Technical success was achieved in 47 patients (84%). Stent placement was antegrade in 36 patients (77%) and retrograde in 11 (23%). Clinical success was achieved in 46/47 (98%) patients who achieved technical success. Adverse events were seen in 13 patients (6 of whom did not achieve technical success) and included bleeding requiring embolization (n = 5), bleeding treated with clips peri-procedurally (n = 1), pancreatitis (n = 5), and a pancreatic fluid collection drained via EUS-drainage (n = 2). The median procedural time was 80 min (range 49-159 min). The CUSUM chart showed that 80-min procedural time was achieved at the 27th procedure. Durations further reduced 40th procedure onward, reaching a plateau indicating proficiency (nonlinear regression P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Endoscopists experienced in EUS-PD are expected to achieve a reduction in procedural time over successive cases, with efficiency reached at 80 min and a learning rate of 27 cases. Continued improvement is demonstrated with additional experience, with plateau indicating mastery suggested at the 40th case. EUS-PD is probably one of the hardest therapeutic endosonographic procedures to learn.
Keywords: EUS-guided pancreatic drainage; pancreatic stricture; pancreatico-jejunostomy; pancreaticogastrostomy; therapeutic EUS.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Learning curve for EUS-guided biliary drainage: What have we learned?Endosc Ultrasound. 2020 Nov-Dec;9(6):392-396. doi: 10.4103/eus.eus_42_20. Endosc Ultrasound. 2020. PMID: 32687074 Free PMC article.
-
EUS-Directed Transgastric Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (EDGE): The First Learning Curve.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul;54(6):569-572. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001326. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32149820
-
EUS-guided gallbladder drainage: a learning curve modified by technical progress.Endosc Int Open. 2020 Jan;8(1):E92-E96. doi: 10.1055/a-1005-6602. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Endosc Int Open. 2020. PMID: 31921991 Free PMC article.
-
EUS guided pancreatic duct decompression in surgically altered anatomy or failed ERCP - A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression.Pancreatology. 2021 Aug;21(5):990-1000. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2021.03.021. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Pancreatology. 2021. PMID: 33865725
-
Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided pancreatic duct access: techniques and literature review of pancreatography, transmural drainage and rendezvous techniques.Dig Endosc. 2013 May;25(3):241-52. doi: 10.1111/den.12048. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Dig Endosc. 2013. PMID: 23490022 Review.
Cited by
-
Current paradigm of endoscopic ultrasound in biliary and pancreatic duct drainage: an update.Ann Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan-Feb;37(1):1-14. doi: 10.20524/aog.2023.0854. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Ann Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38223246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EUS-guided cell transplantation: Planting seeds of hope.Endosc Ultrasound. 2021 Nov-Dec;10(6):401-403. doi: 10.4103/EUS-D-21-00220. Endosc Ultrasound. 2021. PMID: 34975038 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of a novel contrast-enhanced fluoroscopy protocol for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in a phantom model (with video).DEN Open. 2025 Feb 23;5(1):e70087. doi: 10.1002/deo2.70087. eCollection 2025 Apr. DEN Open. 2025. PMID: 39995474 Free PMC article.
-
EUS-guided pancreatic duct drainage with rendezvous technique for post-Whipple pancreatic duct stone.VideoGIE. 2021 Oct 22;6(11):512-515. doi: 10.1016/j.vgie.2021.08.004. eCollection 2021 Nov. VideoGIE. 2021. PMID: 34765846 Free PMC article.
-
Technical review of endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage/anastomosis and trans-endosonographically created route procedures for the treatment of pancreatic diseases.DEN Open. 2024 Jun 7;5(1):e393. doi: 10.1002/deo2.393. eCollection 2025 Apr. DEN Open. 2024. PMID: 38854708 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tessier G, Bories E, Arvanitakis M, et al. EUS-guided pancreatogastrostomy and pancreatobulbostomy for the treatment of pain in patients with pancreatic ductal dilatation inaccessible for transpapillary endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;65:233–41. - PubMed
-
- François E, Kahaleh M, Giovannini M, et al. EUS-guided pancreaticogastrostomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:128–33. - PubMed
-
- Brauer BC, Chen YK, Fukami N, et al. Single-operator EUS-guided cholangiopancreatography for difficult pancreaticobiliary access (with video) Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:471–9. - PubMed
-
- Vila JJ, Pérez-Miranda M, Vazquez-Sequeiros E, et al. Initial experience with EUS-guided cholangiopancreatography for biliary and pancreatic duct drainage: A Spanish national survey. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76:1133–41. - PubMed
-
- Mallery S, Matlock J, Freeman ML. EUS-guided rendezvous drainage of obstructed biliary and pancreatic ducts: Report of 6 cases. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;59:100–7. - PubMed