Patient Characteristics and Outcomes of Nonmetastatic Breast Cancer in Haiti: Results from a Retrospective Cohort
- PMID: 32584461
- PMCID: PMC7485367
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0951
Patient Characteristics and Outcomes of Nonmetastatic Breast Cancer in Haiti: Results from a Retrospective Cohort
Abstract
Background: There are few studies on breast cancer outcomes in the Caribbean region. This study identified a retrospective cohort of female patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer in Haiti and conducted survival analyses to identify prognostic factors that may affect patient outcomes.
Methods: The cohort included 341 patients presenting between June 2012 and December 2016. The primary endpoint was event-free survival (EFS), defined as time to disease progression, recurrence, or death. Descriptive summaries of patient characteristics and treatments were reported. Survival curves were plotted using Kaplan-Meier estimation. Multivariate survival analyses were performed using Cox proportional hazards regression.
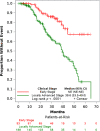
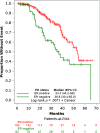
Results: Median age at diagnosis was 49 years, with 64.2% being premenopausal. Most patients (55.1%) were staged as locally advanced. One hundred and sixty patients received neoadjuvant therapy: 33.3% of patients with early stage disease and 61.2% of those with locally advanced stage disease. Curative-intent surgery was performed in 278 (81.5%) patients, and 225 patients received adjuvant therapy. Adjuvant endocrine therapy was used in 82.0% of patients with estrogen receptor-positive disease. During the follow-up period, 28 patients died, 77 had disease recurrence, and 10 had progressive disease. EFS rates at 2 years and 3 years were 80.9% and 63.4%, respectively. After controlling for multiple confounders, the locally advanced stage group had a statistically significant adjusted hazard ratio for EFS of 3.27 compared with early stage.
Conclusion: Patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer in Haiti have more advanced disease, poorer prognostic factors, and worse outcomes compared with patients in high-income countries. Despite several limitations, curative treatment is possible in Haiti.
Implications for practice: Patients with breast cancer in Haiti have poor outcomes. Prior studies show that most Haitian patients are diagnosed at later stages. However, there are no rigorous studies describing how late-stage diagnosis and other prognostic factors affect outcomes in this population. This study presents a detailed analysis of survival outcomes and assessment of prognostic factors in patients with nonmetastatic breast cancer treated in Haiti. In addition to late-stage diagnosis, other unfavorable prognostic factors identified were young age and estrogen receptor-negative disease. The study also highlights that the availability of basic breast cancer treatment in Haiti can lead to promising early patient outcomes.
Keywords: Breast cancer outcomes; Cancer in low-resource settings; Caribbean region; Global oncology; Haiti.
© 2020 The Authors. The Oncologist published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of AlphaMed Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Bray F, Ferlay J et al. International variation in female breast cancer incidence and mortality rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2015;24:1495–1506. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Population fact sheets. International Agency for Research on Cancer Web site. Available at https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-populations. Accessed April 26, 2018.
-
- Razzaghi H, Quesnel‐Crooks S, Sherman R et al. Leading causes of cancer mortality ‐ Caribbean region, 2003–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016;65,:1395–1400. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

