Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Large Biosynthetic Gene Clusters via Oligonucleotide Recombineering and CRISPR/Cas9 Targeting
- PMID: 32584552
- PMCID: PMC8142379
- DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00265
Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Large Biosynthetic Gene Clusters via Oligonucleotide Recombineering and CRISPR/Cas9 Targeting
Abstract
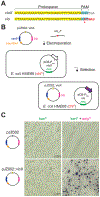
Genetic engineering of natural product biosynthetic gene clusters represents an attractive approach to access new and complex bioactive small molecules. However, due to the large number and size of some genes involved in specialized metabolism, notably those encoding modular polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase megaproteins, it remains difficult to introduce precise genetic mutations to probe domain activity or alter chemical product formation. Here, we report the development and validation of a robust method combining oligonucleotide recombineering and CRISPR/Cas9 targeting for rapid site-directed mutagenesis of cloned pathways, which can be directly transferred to a heterologous host for expression. We rapidly generated 12 point mutations and identified several important determinants of successful mutagenesis, including the protospacer/PAM sequence and presence of regions of local homology. Our approach may be broadly applicable for researchers interested in probing natural product biosynthesis or performing pathway engineering.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; biosynthetic gene cluster; heterologous expression; natural product; recombineering; site-directed mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Davies J, and Ryan KS (2012) Introducing the parvome: bioactive compounds in the microbial world. ACS Chem. Biol 7, 252–259. - PubMed
-
- Thirlway J, Lewis R, Nunns L, Al Nakeeb M, Styles M, Struck AW, Smith CP, and Micklefield J (2012) Introduction of a non-natural amino acid into a nonribosomal peptide antibiotic by modification of adenylation domain specificity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 51, 7181–7184. - PubMed
-
- Court DL, Swaminathan S, Yu D, Wilson H, Baker T, Bubunenko M, Sawitzke J, and Sharan SK (2003) Mini-lambda: a tractable system for chromosome and BAC engineering. Gene 315, 63–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

