Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness
- PMID: 32584597
- PMCID: PMC7491404
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC
Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness
Abstract
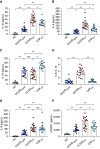
Rationale: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a global threat to health. Its inflammatory characteristics are incompletely understood.Objectives: To define the cytokine profile of COVID-19 and to identify evidence of immunometabolic alterations in those with severe illness.Methods: Levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and sTNFR1 (soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 1) were assessed in plasma from healthy volunteers, hospitalized but stable patients with COVID-19 (COVIDstable patients), patients with COVID-19 requiring ICU admission (COVIDICU patients), and patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia requiring ICU support (CAPICU patients). Immunometabolic markers were measured in circulating neutrophils from patients with severe COVID-19. The acute phase response of AAT (alpha-1 antitrypsin) to COVID-19 was also evaluated.Measurements and Main Results: IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and sTNFR1 were all increased in patients with COVID-19. COVIDICU patients could be clearly differentiated from COVIDstable patients, and demonstrated higher levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and sTNFR1 but lower IL-10 than CAPICU patients. COVID-19 neutrophils displayed altered immunometabolism, with increased cytosolic PKM2 (pyruvate kinase M2), phosphorylated PKM2, HIF-1α (hypoxia-inducible factor-1α), and lactate. The production and sialylation of AAT increased in COVID-19, but this antiinflammatory response was overwhelmed in severe illness, with the IL-6:AAT ratio markedly higher in patients requiring ICU admission (P < 0.0001). In critically unwell patients with COVID-19, increases in IL-6:AAT predicted prolonged ICU stay and mortality, whereas improvement in IL-6:AAT was associated with clinical resolution (P < 0.0001).Conclusions: The COVID-19 cytokinemia is distinct from that of other types of pneumonia, leading to organ failure and ICU need. Neutrophils undergo immunometabolic reprogramming in severe COVID-19 illness. Cytokine ratios may predict outcomes in this population.
Keywords: COVID-19; alpha-1 antitrypsin; cytokines; immunometabolism; neutrophils.
Figures


Comment in
-
Rewiring the Immune Response in COVID-19.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Sep 15;202(6):784-786. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202007-2934ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32755507 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is IL-6 the Right Target in COVID-19 Severe Pneumonia?Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Jan 1;203(1):139-140. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202007-2924LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 32955921 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Blot et al. and to Inoue et al.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Jan 1;203(1):141-142. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202008-3169LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 32955924 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of IL-6 in Severe Inflammation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Jan 1;203(1):140-141. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202007-3001LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 32955926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): situation report–150. 2020 Jun 18 [accessed 2020 Jun 18]. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2....
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. [online ahead of print] 24 Feb 2020; DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. - PubMed
-
- Palsson-McDermott EM, Curtis AM, Goel G, Lauterbach MA, Sheedy FJ, Gleeson LE, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1α activity and IL-1β induction and is a critical determinant of the warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cell Metab. 2015;21:65–80. [Published erratum appears in Cell Metab 21:347.] - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

