SIRT6 mono-ADP ribosylates KDM2A to locally increase H3K36me2 at DNA damage sites to inhibit transcription and promote repair
- PMID: 32584788
- PMCID: PMC7343504
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103567
SIRT6 mono-ADP ribosylates KDM2A to locally increase H3K36me2 at DNA damage sites to inhibit transcription and promote repair
Abstract
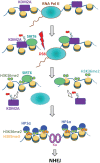
When transcribed DNA is damaged, the transcription and DNA repair machineries must interact to ensure successful DNA repair. The mechanisms of this interaction in the context of chromatin are still being elucidated. Here we show that the SIRT6 protein enhances non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) DNA repair by transiently repressing transcription. Specifically, SIRT6 mono-ADP ribosylates the lysine demethylase JHDM1A/KDM2A leading to rapid displacement of KDM2A from chromatin, resulting in increased H3K36me2 levels. Furthermore, we found that through HP1α binding, H3K36me2 promotes subsequent H3K9 tri-methylation. This results in transient suppression of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II and recruitment of NHEJ factors to DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs). These data reveal a mechanism where SIRT6 mediates a crosstalk between transcription and DNA repair machineries to promote DNA repair. SIRT6 functions in multiple pathways related to aging, and its novel function coordinating DNA repair and transcription is yet another way by which SIRT6 promotes genome stability and longevity.
Keywords: DNA repair; SIRT6; genome stability; longevity; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
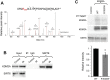
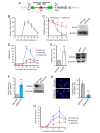
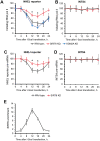
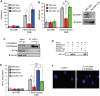
References
-
- Kakarougkas A, Ismail A, Chambers AL, Riballo E, Herbert AD, Künzel J, Löbrich M, Jeggo PA, Downs JA. Requirement for PBAF in transcriptional repression and repair at DNA breaks in actively transcribed regions of chromatin. Mol Cell. 2014; 55:723–32. 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.06.028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

