Using structured pathology data to predict hospital-wide mortality at admission
- PMID: 32584872
- PMCID: PMC7316243
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235117
Using structured pathology data to predict hospital-wide mortality at admission
Abstract
Early prediction of in-hospital mortality can improve patient outcome. Current prediction models for in-hospital mortality focus mainly on specific pathologies. Structured pathology data is hospital-wide readily available and is primarily used for e.g. financing purposes. We aim to build a predictive model at admission using the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes as predictors and investigate the effect of the self-evident DNR ("Do Not Resuscitate") diagnosis codes and palliative care codes. We compare the models using ICD-10-CM codes with Risk of Mortality (RoM) and Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) as predictors using the Random Forests modeling approach. We use the Present on Admission flag to distinguish which diagnoses are present on admission. The study is performed in a single center (Ghent University Hospital) with the inclusion of 36 368 patients, all discharged in 2017. Our model at admission using ICD-10-CM codes (AUCROC = 0.9477) outperforms the model using RoM (AUCROC = 0.8797 and CCI (AUCROC = 0.7435). We confirmed that DNR and palliative care codes have a strong impact on the model resulting in a decrease of 7% for the ICD model (AUCROC = 0.8791) at admission. We therefore conclude that a model with a sufficient predictive performance can be derived from structured pathology data, and if real-time available, can serve as a prerequisite to develop a practical clinical decision support system for physicians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


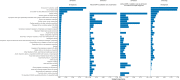
References
-
- Clermont G, Angus DC, DiRusso SM, Griffin M, Linde-Zwirble WT. Predicting hospital mortality for patients in the intensive care unit: A comparison of artificial neural networks with logistic regression models. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(2):291–6. 10.1097/00003246-200102000-00012 PubMed PMID: WOS:000167179400011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allyn J, Allou N, Augustin P, Philip I, Martinet O, Belghiti M, et al. A Comparison of a Machine Learning Model with EuroSCORE II in Predicting Mortality after Elective Cardiac Surgery: A Decision Curve Analysis. Plos One. 2017;12(1). 10.1371/journal.pone.0169772 PubMed PMID: WOS:000391641500136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

