Mapping QTLs for enhancing early biomass derived from Aegilops tauschii in synthetic hexaploid wheat
- PMID: 32584908
- PMCID: PMC7316292
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234882
Mapping QTLs for enhancing early biomass derived from Aegilops tauschii in synthetic hexaploid wheat
Abstract
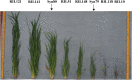
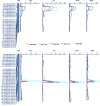
Strong early vigour plays a crucial role in wheat yield improvement by enhancing resource utilization efficiency. Synthetic hexaploid wheat (SHW) combines the elite genes of tetraploid wheat with Aegilops tauschii and has been widely used in wheat genetic improvement for its abundant genetic variation. The two SHWs Syn79 and Syn80 were derived from the crossing of the same tetraploid wheat DOY1 with two different Ae. tauschii accessions, AT333 and AT428, respectively. The Syn80 possessed better early vigour traits than Syn79, theretically caused by their D genome from Ae. tauschii. To dissect their genetic basis in a hexaploid background, 203 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from the cross of Syn79 x Syn80 were developed to detect quantitative trait loci (QTL) for four early biomass related traits: plant height (PH), tiller number (TN), shoot fresh weight (SFW) and shoot dry weight (SDW) per plant, under five different environmental conditions. Determined from the data of SNP markers, two genome regions on 1DS and 7D were stably associated with the four early biomass related traits showing pleiotropic effects. Four stable QTLs QPh.saas-1DS, QTn.saas-1DS, QSfw.saas-1DS and QSdw.saas-1DS explaining 7.92, 15.34, 9.64 and 10.15% of the phenotypic variation, respectively, were clustered in the region of 1DS from AX-94812958 to AX-110910133. Meanwhile, QPh.saas-7D, QTn.saas-7D, QSfw.saas-7D and QSdw.saas-7D were flanked by AX-109917900 and AX-110605376 on 7D, explaining 16.12, 24.35, 15.25 and 13.37% of the phenotypic variation on average, respectively. Moreover, these genomic QTLs on 1DS and 7D enhancing biomass in the parent Syn80 were from Ae. tauschii AT428. These findings suggest that these two QTLs from Ae. tauschii can be expressed stably in a hexaploid background at the jointing stage and be used for wheat improvement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quantitative trait locus analysis for flowering-related traits using two F2 populations derived from crosses between Japanese common wheat cultivars and synthetic hexaploids.Genes Genet Syst. 2015;90(2):89-98. doi: 10.1266/ggs.90.89. Genes Genet Syst. 2015. PMID: 26399768
-
Genetic and physiological architecture of early vigor in Aegilops tauschii, the D-genome donor of hexaploid wheat. A quantitative trait loci analysis.Plant Physiol. 2005 Oct;139(2):1078-94. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.063263. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16183848 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and molecular characterization of Hessian fly resistance in diploid wheat, Aegilops tauschii.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Oct 22;19(1):439. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2058-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31640550 Free PMC article.
-
Broadening the bread wheat D genome.Theor Appl Genet. 2019 May;132(5):1295-1307. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03299-z. Epub 2019 Feb 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2019. PMID: 30739154 Review.
-
Synthetic hexaploid wheat and its utilization for wheat genetic improvement in China.J Genet Genomics. 2009 Sep;36(9):539-46. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60145-9. J Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19782955 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association study for seedling biomass-related traits in Gossypium arboreum L.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jan 27;22(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03443-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35086471 Free PMC article.
-
Pentaploidization Enriches the Genetic Diversity of Wheat by Enhancing the Recombination of AB Genomes.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 29;13:883868. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.883868. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35845672 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Improvement and Application Practices of Synthetic Hexaploid Wheat.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 21;14(2):283. doi: 10.3390/genes14020283. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kihara H. Discovery of the DD-analyser, one of the ancestors of Triticum vulgare. Agric Hortic. 1944; 19: 889–890.
-
- Dvorak J, Luo MC, Yang ZL, Zhang HB. The structure of the Aegilops tauschii genepool and the evolution of hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet. 1998; 97: 657–670.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

