Incremental Benefit of Achieving Endoscopic and Histologic Remission in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32585306
- PMCID: PMC7658293
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.043
Incremental Benefit of Achieving Endoscopic and Histologic Remission in Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background & aims: Clinical remission, defined by a composite of patient reported outcomes and Mayo endoscopy subscore (MES) 0 or 1 is a recommended treatment target in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC). We estimated whether incorporating more rigorous remission definitions, of endoscopic remission (MES 0) and histologic remission, affects risk of relapse.
Methods: Through a systematic review, we identified cohort studies in adults with UC in clinical remission that reported a minimum 12-month risk of clinical relapse, based on MES (0 vs 1) and/or histologic disease activity, in patients with endoscopic remission. Using random effects meta-analysis, we calculated relative and absolute risk of clinical relapse in patients with UC achieving different treatment targets.
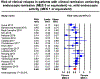
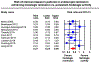
Results: In a meta-analysis of 17 studies that included 2608 patients with UC in clinical remission, compared to patients achieving MES 1, patients achieving MES 0 had a 52% lower risk of clinical relapse (relative risk, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.37-0.62). The median 12-month risk of clinical relapse in patients with MES 1 was 28.7%; the estimated annual risk of clinical relapse in patients with MES 0 was 13.7% (95% CI, 10.6-17.9). In a meta-analysis of 10 studies in patients in endoscopic remission (MES 0), patients who achieved histologic remission had a 63% lower risk of clinical relapse vs patients with persistent histologic activity (relative risk, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.24-0.56). Estimated annual risk of clinical relapse in who achieved achieving histologic remission was 5.0% (95% CI, 3.3-7.7).
Conclusions: In a systematic review and meta-analysis of patients with UC in clinical remission, we observed that patients achieving more rigorous treatment endpoints (endoscopic and histologic remission) have a substantially lower risk of clinical relapse compared with patients achieving clinical remission.
Keywords: Abdominal Pain; Biopsy; IBD; Inflammation; Inflammatory Bowel Disease; Treat-to-Target.
Copyright © 2020 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest:
• Hyuk Yoon: No conflicts of interest
• Sushrut Jangi: No conflicts of interest
• Parambir Dulaihas received research support from Takeda, Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Polymedco, ALPCO, Buhlmann, and consulting fees from Takeda, Pfizer, Abbvie and Janssen.
• Brigid Boland has received research support from Takeda and Janssen, and consulting fees from Abbvie and Prometheus laboratories.
• Larry Prokop: No conflicts of interest
• Vipul Jairath has received has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Arena pharmaceuticals, Genetech, Pendopharm, Sandoz, Merck, Takeda, Janssen, Robarts Clinical Trials, Topivert, Celltrion; speaker’s fees from Takeda, Janssen, Shire, Ferring, Abbvie, Pfizer.
• Brian Feagan has received grant/research support from Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Tillotts Pharma, AbbVie, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Centocor, Elan/Biogen, UCB Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, ActoGenix and Wyeth Pharmaceuticals; consulting fees from Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Merck, Centocor, Elan/Biogen, Janssen-Ortho, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, UCB Pharma, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Serono, Genentech, Tillotts Pharma, Unity Pharmaceuticals, Albireo Pharma, Given Imaging, Salix Pharmaceuticals, Novonordisk, GSK, ActoGenix, Prometheus Therapeutics and Diagnostics, Athersys, Axcan, Gilead, Pfizer, Shire, Wyeth, Zealand Pharma, Zyngenia, GiCare Pharma and Sigmoid Pharma; and speaker’s bureau fees from UCB, AbbVie and J&J/Janssen.
• William Sandborn has received research grants from Atlantic Healthcare Limited, Amgen, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Abbvie, Janssen, Takeda, Lilly, Celgene/Receptos,Pfizer, Prometheus Laboratories (now Prometheus Biosciences); consulting fees from Abbvie, Allergan, Amgen, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Avexegen Therapeutics, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Celltrion, Conatus, Cosmo, Escalier Biosciences, Ferring, Forbion, Genentech, Gilead Sciences, Gossamer Bio, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin Pharmaceutical Research, Landos Biopharma, Lilly, Oppilan Pharma, Otsuka, Pfizer, Progenity, Prometheus Biosciences (merger of Precision IBD and Prometheus Laboratories), Reistone, Ritter Pharmaceuticals, Robarts Clinical Trials (owned by Health Academic Research Trust, HART), Series Therapeutics, Shire, Sienna Biopharmaceuticals, Sigmoid Biotechnologies, Sterna Biologicals, Sublimity Therapeutics, Takeda, Theravance Biopharma, Tigenix, Tillotts Pharma, UCB Pharma, Ventyx Biosciences, Vimalan Biosciences, Vivelix Pharmaceuticals; and stock or stock options from BeiGene, Escalier Biosciences, Gossamer Bio, Oppilan Pharma, Prometheus Biosciences (merger of Precision IBD and Prometheus Laboratories), Progenity, Ritter Pharmaceuticals, Ventyx Biosciences, Vimalan Biosciences. Spouse: Opthotech - consultant, stock options; Progenity - consultant, stock; Oppilan Pharma - employee, stock options; Escalier Biosciences - employee, stock options; Prometheus Biosciences (merger of Precision IBD and Prometheus Laboratories) - employee, stock options; Ventyx Biosciences – employee, stock options; Vimalan Biosciences – employee, stock options.
• Siddharth Singh has received research grants from AbbVie and Janssen, and personal fees from Takeda and Pfizer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endoscopic mucosal healing and histologic remission in ulcerative colitis: a systematic literature review of clinical, quality-of-life and economic outcomes.Curr Med Res Opin. 2022 Sep;38(9):1531-1541. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2022.2081453. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Curr Med Res Opin. 2022. PMID: 35608153
-
Ulcerative colitis patients in clinical remission demonstrate correlations between fecal immunochemical test results, mucosal healing, and risk of relapse.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 7;22(21):5079-87. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i21.5079. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27275100 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors and outcomes of histological remission in ulcerative colitis treated to endoscopic healing.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Sep;52(6):1008-1016. doi: 10.1111/apt.16026. Epub 2020 Aug 9. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33119168 Free PMC article.
-
Histologic remission does not offer additional benefit for ulcerative colitis patients in endoscopic remission.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Dec;52(11-12):1676-1682. doi: 10.1111/apt.16147. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33131108
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis: the advantage of endoscopic Mayo score 0 over 1 in patients with ulcerative colitis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Mar 3;22(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02157-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35240984 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Resolving Histological Inflammation in Ulcerative Colitis With Mirikizumab in the LUCENT Induction and Maintenance Trial Programmes.J Crohns Colitis. 2023 Oct 20;17(9):1457-1470. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad050. J Crohns Colitis. 2023. PMID: 37057827 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Applying Biomarkers in Treat-to-target Approach for IBD.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025 Jun 20;27(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s11894-025-00991-7. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40540152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treat-to-target of endoscopic remission in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in symptomatic remission on advanced therapies (QUOTIENT): rationale, design and protocol for an open-label, multicentre, pragmatic, randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2025 Mar 31;12(1):e001615. doi: 10.1136/bmjgast-2024-001615. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40164445 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological assessment of the microscopic activity in inflammatory bowel diseases: What are we looking for?World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Sep 28;28(36):5300-5312. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i36.5300. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36185628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new endoscopic scoring system corresponding to histological healing using linked color imaging in ulcerative colitis: the SOUL study.Endosc Int Open. 2023 May 17;11(5):E504-E512. doi: 10.1055/a-2067-8943. eCollection 2023 May. Endosc Int Open. 2023. PMID: 37206692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubin DT, Ananthakrishnan AN, Siegel CA, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Ulcerative Colitis in Adults. Am J Gastroenterol 2019;114:384–413. - PubMed
-
- Harbord M, Eliakim R, Bettenworth D, et al. Third European Evidence-based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 2: Current Management. J Crohns Colitis 2017;11:769–784. - PubMed
-
- Sands BE, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, et al. Ustekinumab as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis. N Engl J Med 2019;381:1201–1214. - PubMed
-
- Park S, Abdi T, Gentry M, et al. Histological Disease Activity as a Predictor of Clinical Relapse Among Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2016;111:1692–1701. - PubMed
-
- Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000;283:2008–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

