A longitudinal examination of plasma neurofilament light and total tau for the clinical detection and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 32585491
- PMCID: PMC7484086
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.05.011
A longitudinal examination of plasma neurofilament light and total tau for the clinical detection and monitoring of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
We examined baseline and longitudinal associations between plasma neurofilament light (NfL) and total tau (t-tau), and the clinical presentation of Alzheimer's disease (AD). A total of 579 participants (238, normal cognition [NC]; 185, mild cognitive impairment [MCI]; 156, AD dementia) had baseline blood draws; 82% had follow-up evaluations. Plasma samples were analyzed for NfL and t-tau using Simoa technology. Baseline plasma NfL was higher in AD dementia than MCI (standardized mean difference = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.37-0.73) and NC (standardized mean difference = 0.68, 95% CI: 0.49-0.88), corresponded to Clinical Dementia Rating scores (OR = 1.94, 95% CI: 1.35-2.79]), and correlated with all neuropsychological tests (r's = 0.13-0.42). Longitudinally, NfL did not predict diagnostic conversion but predicted decline on 3/10 neuropsychological tests. Baseline plasma t-tau was higher in AD dementia than NC with a small effect (standardized mean difference = 0.33, 95% CI: 0.10-0.57) but not MCI. t-tau did not statistically significant predict any longitudinal outcomes. Plasma NfL may be useful for the detection of AD dementia and monitoring of disease progression. In contrast, there was minimal evidence in support of plasma t-tau.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Neurofilament light; Plasma biomarkers; Total tau.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

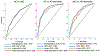
References
-
- Albani D, Marizzoni M, Ferrari C, Fusco F, Boeri L, Raimondi I, Jovicich J, Babiloni C, Soricelli A, Lizio R, Galluzzi S, Cavaliere L, Didic M, Schonknecht P, Molinuevo JL, Nobili F, Parnetti L, Payoux P, Bocchio L, Salvatore M, Rossini PM, Tsolaki M, Visser PJ, Richardson JC, Wiltfang J, Bordet R, Blin O, Forloni G, Frisoni GB, PharmaCog C Plasma Abeta42 as a Biomarker of Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease Progression in Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: Evidence from the PharmaCog/E-ADNI Study. J Alzheimers Dis 2019; 69: 37–48. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180321 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alosco ML, Sugarman MA, Besser LM, Tripodis Y, Martin B, Palmisano JN, Kowall NW, Au R, Mez J, DeCarli C, Stein TD, McKee AC, Killiany RJ, Stern RA. A Clinicopathological Investigation of White Matter Hyperintensities and Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology. J Alzheimers Dis 2018; 63: 1347–1360. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alosco ML, Tripodis Y, Jarnagin J, Baugh CM, Martin B, Chaisson CE, Estochen N, Song L, Cantu RC, Jeromin A, Stern RA. Repetitive head impact exposure and later-life plasma total tau in former National Football League players. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 2017; 7: 33–40. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2016.11.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

