Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation Modulates Prefrontal Cortex Oxygenation during Submaximal Exercise Testing in Cardiovascular Disease Patients
- PMID: 32585816
- PMCID: PMC7349315
- DOI: 10.3390/bs10060104
Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation Modulates Prefrontal Cortex Oxygenation during Submaximal Exercise Testing in Cardiovascular Disease Patients
Abstract
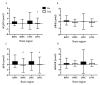
The purpose of this study was to investigate if prefrontal cortex (PFC) oxygenation during incremental exercise is altered among cardiovascular disease (CVD) patients who completed 6 weeks of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation (CR). Nineteen (male = 14, female = 5; 65.5 ± 11.5 years) participants from an outpatient CR program were enrolled in the study. Each participant completed a submaximal graded treadmill evaluation at intake and again upon completion of 18 individualized CR sessions. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) imaging was used to measure left- and right- PFC (LPFC and RPFC) oxygenation parameters during the submaximal exercise evaluations. Patients showed improvements in cardiorespiratory capacity (pre 5.5 ± 2.5 vs. post 6.9 ± 2.8 metabolic equivalents (METs)). A significant decrease in LPFC and RPFC oxygenation was observed during the post-CR exercise test compared to pre-CR. CVD patients enrolled in 6 weeks of CR showed significant improvements in functional capacity along with decreased cortical oxygenation during submaximal exercise. Exercise training may cause distribution of cortical resources to motor regions that support sustained exercise.
Keywords: aerobic exercise; cardiac rehabilitation; cardiovascular disease; oxygenation; prefrontal cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exercise-Based Cardiac Rehabilitation Improves Cognitive Function Among Patients With Cardiovascular Disease.J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2020 Nov;40(6):407-413. doi: 10.1097/HCR.0000000000000545. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2020. PMID: 32947322
-
Exercise Intensity Influences Prefrontal Cortex Oxygenation during Cognitive Testing.Behav Sci (Basel). 2019 Jul 26;9(8):83. doi: 10.3390/bs9080083. Behav Sci (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31357450 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer and cardiovascular disease: The impact of cardiac rehabilitation and cardiorespiratory fitness on survival.Int J Cardiol. 2021 Nov 15;343:139-145. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.09.004. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Int J Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34506825 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Cardiorespiratory Fitness on Cerebral Oxygenation in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 4;13:838450. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.838450. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35309063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prefrontal Cortex Oxygenation During Endurance Performance: A Systematic Review of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Studies.Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 26;12:761232. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.761232. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34764885 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Caparas S.N., Clair M.J., Krombach S.R., Hendrick J.W., Houck W.V., Kribbs S.B., Mukherjee R., Tempel G.E., Spinale F.G. Brain Blood Flow Patterns after the Development of Congestive Heart Failure: Effects of Treadmill Exercise. Crit. Care Med. 2000;28:209–214. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200001000-00034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Servey J., Stephens M.B. Cardiac Rehabilitation: Improving Function and Reducing Risk. Am. Fam. Physician. 2016;94:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Kodama S., Saito K., Tanaka S., Maki M., Yachi Y., Asumi M., Sugawara A., Totsuka K., Shimano H., Ohashi Y. Cardiorespiratory Fitness as a Quantitative Predictor of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Healthy Men and Women: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA. 2009;301:2024–2035. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.681. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

