A Peptidic Thymidylate-Synthase Inhibitor Loaded on Pegylated Liposomes Enhances the Antitumour Effect of Chemotherapy Drugs in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells
- PMID: 32585842
- PMCID: PMC7352236
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21124452
A Peptidic Thymidylate-Synthase Inhibitor Loaded on Pegylated Liposomes Enhances the Antitumour Effect of Chemotherapy Drugs in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells
Abstract
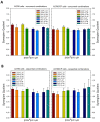
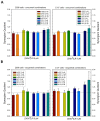
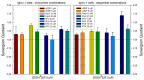
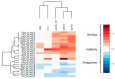
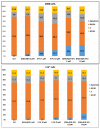
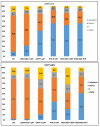
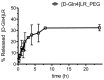
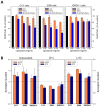
There is currently no effective long-term treatment for ovarian cancer (OC) resistant to poly-chemotherapy regimens based on platinum drugs. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated a strong association between development of Pt-drug resistance and increased thymidylate synthase (hTS) expression, and the consequent cross-resistance to the hTS inhibitors 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and raltitrexed (RTX). In the present work, we propose a new tool to combat drug resistance. We propose to treat OC cell lines, both Pt-sensitive and -resistant, with dual combinations of one of the four chemotherapeutic agents that are widely used in the clinic, and the new peptide, hTS inhibitor, [D-Gln4]LR. This binds hTS allosterically and, unlike classical inhibitors that bind at the catalytic pocket, causes cell growth inhibition without inducing hTS overexpression. The dual drug combinations showed schedule-dependent synergistic antiproliferative and apoptotic effects. We observed that the simultaneous treatment or 24h pre-treatment of OC cells with the peptide followed by either agent produced synergistic effects even in resistant cells. Similar synergistic or antagonistic effects were obtained by delivering the peptide into OC cells either by means of a commercial delivery system (SAINT-PhD) or by pH sensitive PEGylated liposomes. Relative to non-PEGylated liposomes, the latter had been previously characterized and found to allow macrophage escape, thus increasing their chance to reach the tumour tissue. The transition from the SAINT-PhD delivery system to the engineered liposomes represents an advancement towards a more drug-like delivery system and a further step towards the use of peptides for in vivo studies. Overall, the results suggest that the association of standard drugs, such as cDDP and/or 5-FU and/or RTX, with the novel peptidic TS inhibitor encapsulated into PEGylated pH-sensitive liposomes can represent a promising strategy for fighting resistance to cDDP and anti-hTS drugs.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; drug-resistance; human thymidylate synthase peptidic-inhibitors; ovarian cancer; pH-sensitive PEGylated liposomes; raltitrexed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A rationale for the clinical development of the thymidylate synthase inhibitor ZD9331 in ovarian and other solid tumours.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):215-23. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00084-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12084463 Review.
-
pH-Promoted Release of a Novel Anti-Tumour Peptide by "Stealth" Liposomes: Effect of Nanocarriers on the Drug Activity in Cis-Platinum Resistant Cancer Cells.Pharm Res. 2018 Sep 12;35(11):206. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2489-z. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30209680
-
Antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in combination with 5-fluorouracil and the thymidylate synthase inhibitor AG337 in human colon, breast and ovarian cancers.Anticancer Drugs. 1997 Oct;8(9):876-85. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199710000-00009. Anticancer Drugs. 1997. PMID: 9402315
-
Human Thymidylate Synthase Inhibitors Halting Ovarian Cancer Growth.Vitam Horm. 2018;107:473-513. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2017.12.002. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Vitam Horm. 2018. PMID: 29544641 Review.
-
Conveying a newly designed hydrophilic anti-human thymidylate synthase peptide to cisplatin resistant cancer cells: are pH-sensitive liposomes more effective than conventional ones?Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017 Mar;43(3):465-473. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2016.1262870. Epub 2016 Dec 26. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017. PMID: 27885848
Cited by
-
A bioinformatic analysis: the overexpression and clinical significance of FCGBP in ovarian cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Mar 3;13(5):7416-7429. doi: 10.18632/aging.202601. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33686968 Free PMC article.
-
FOXD1 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with macrophages infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Biosci Rep. 2021 Jul 30;41(7):BSR20202929. doi: 10.1042/BSR20202929. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34028536 Free PMC article.
-
Renovation as innovation: Repurposing human antibacterial peptide LL-37 for cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 23;13:944147. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.944147. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36081952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Formation of Chitosan-Coated Rhamnolipid Liposomes Containing Curcumin: Stability and In Vitro Digestion.Molecules. 2021 Jan 21;26(3):560. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030560. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33494543 Free PMC article.
-
Folic Acid-Peptide Conjugates Combine Selective Cancer Cell Internalization with Thymidylate Synthase Dimer Interface Targeting.J Med Chem. 2021 Mar 25;64(6):3204-3221. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02107. Epub 2021 Mar 12. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33710891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyer Q., Li C., Lee J.Y., Shepard H.M. A novel approach to thymidylate synthase as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:446–452. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

