Maackiain Ameliorates 6-Hydroxydopamine and SNCA Pathologies by Modulating the PINK1/Parkin Pathway in Models of Parkinson's Disease in Caenorhabditis elegans and the SH-SY5Y Cell Line
- PMID: 32585871
- PMCID: PMC7352553
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21124455
Maackiain Ameliorates 6-Hydroxydopamine and SNCA Pathologies by Modulating the PINK1/Parkin Pathway in Models of Parkinson's Disease in Caenorhabditis elegans and the SH-SY5Y Cell Line
Abstract
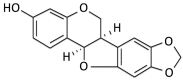
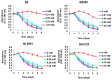
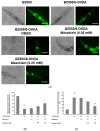
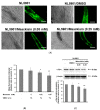
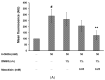
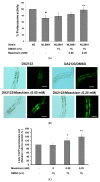
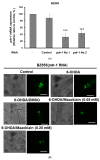
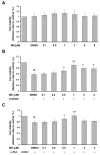
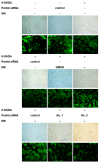
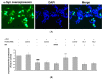
The movement disorder Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most frequently diagnosed neurodegenerative disease, and is associated with aging, the environment, and genetic factors. The intracellular aggregation of α-synuclein and the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta are the pathological hallmark of PD. At present, there is no successful treatment for PD. Maackiain (MK) is a flavonoid extracted from dried roots of Sophora flavescens Aiton. MK has emerged as a novel agent for PD treatment that acts by inhibiting monoamine oxidase B. In this study, we assessed the neuroprotective potential of MK in Caenorhabditis elegans and investigated possible mechanism of this neuroprotection in the human SH-SY5Y cell line. We found that MK significantly reduced dopaminergic neuron damage in 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-exposed worms of the BZ555 strain, with corresponding improvements in food-sensing behavior and life-span. In transgenic worms of strain NL5901 treated with 0.25 mM MK, the accumulation of α-synuclein was diminished by 27% (p < 0.01) compared with that in untreated worms. Moreover, in worms and the SH-SY5Y cell line, we confirmed that the mechanism of MK-mediated protection against PD pathology may include blocking apoptosis, enhancing the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and augmenting autophagy by increasing PINK1/parkin expression. The use of small interfering RNA to downregulate parkin expression in vivo and in vitro could reverse the benefits of MK in PD models. MK may have considerable therapeutic applications in PD.
Keywords: 6-Hydroxydopamine; Caenorhabditis elegans; Parkinson’s disease; SH-SY5Y cell; apoptosis; autophagy; maackiain; parkin; proteasome; α-Synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Calabrese V., Santoro A., Monti D., Crupi R., Di Paola R., Latteri S., Cuzzocrea S., Zappia M., Giordano J., Calabrese E.J., et al. Aging and Parkinson’s Disease: Inflammaging, neuroinflammation and biological remodeling as key factors in pathogenesis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018;115:80–91. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.10.379. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bouca-Machado R., Duarte G.S., Patriarca M., Castro Caldas A., Alarcao J., Fernandes R.M., Mestre T.A., Matias R., Ferreira J.J. Measurement Instruments to Assess Functional Mobility in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020;7:129–139. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.12874. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

