Molecular Bases of Drug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32585893
- PMCID: PMC7352164
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12061663
Molecular Bases of Drug Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
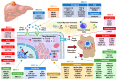
The poor outcome of patients with non-surgically removable advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most frequent type of primary liver cancer, is mainly due to the high refractoriness of this aggressive tumor to classical chemotherapy. Novel pharmacological approaches based on the use of inhibitors of tyrosine kinases (TKIs), mainly sorafenib and regorafenib, have provided only a modest prolongation of the overall survival in these HCC patients. The present review is an update of the available information regarding our understanding of the molecular bases of mechanisms of chemoresistance (MOC) with a significant impact on the response of HCC to existing pharmacological tools, which include classical chemotherapeutic agents, TKIs and novel immune-sensitizing strategies. Many of the more than one hundred genes involved in seven MOC have been identified as potential biomarkers to predict the failure of treatment, as well as druggable targets to develop novel strategies aimed at increasing the sensitivity of HCC to pharmacological treatments.
Keywords: DNA repair; apoptosis; cancer stem cell; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; liver cancer; metabolism; multidrug resistance; refractoriness; transport; tumor environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Marin J.J.G., Briz O., Herraez E., Lozano E., Asensio M., Di Giacomo S., Romero M.R., Osorio-Padilla L.M., Santos-Llamas A.I., Serrano M.A., et al. Molecular bases of the poor response of liver cancer to chemotherapy. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2018;42:182–192. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2017.12.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm S.M., Adnane L., Newell P., Villanueva A., Llovet J.M., Lynch M. Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008;7:3129–3140. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources