Generation of esophageal organoids and organotypic raft cultures from human pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 32586439
- PMCID: PMC8056392
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2020.04.009
Generation of esophageal organoids and organotypic raft cultures from human pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
The human and murine esophagus have some substantial differences that limit the utility of mouse as a model to study human esophagus development and disease. Due to these limitations several recent reports describe the development of methods to generate human esophageal tissues via the directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. Methods for differentiation are based on knowledge of years of studying embryonic development of the esophagus in vertebrate animal models. Esophageal tissues derived from human pluripotent stem cells have been used to study both development and diseases affecting the esophagus. Here, we provide a detailed protocol for the directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into human esophageal organoids and organotypic raft cultures, that are highly similar, morphologically and transcriptionally, to the human esophagus epithelium. We discuss limitations of the current esophageal models and the importance of engineering more complex tissue models with muscle and enteric nerves. Moving forward, these models might be utilized for the development of personalized treatments, as well as other therapeutic solutions.
Keywords: Anterior foregut; Definitive endoderm; Esophageal organoids; Esophageal raft cultures; Human pluripotent stem cells.
© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
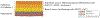
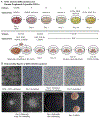
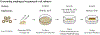
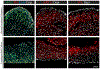
References
-
- Haeri H, Mardany O, Asadi-Amoli F, & Shahsiah R (2013). Human papilloma virus and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Medica Iranica, 51 (4), 242–245. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23690103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

