Generation of multi-cellular human liver organoids from pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 32586449
- PMCID: PMC8011941
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2020.03.009
Generation of multi-cellular human liver organoids from pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
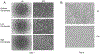
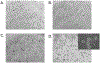
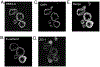
A growing number of in vitro hepatic models exist to study human genetics, liver biology, disease modeling and drug development and range from 2D hepatocytes to 3D multi-cellular tissues that are derived from human stem cells. However, stem cell-based models generally suffer from batch-, clone- and donor-dependent variability, hindering broader usage in diverse biomedical applications. To circumvent this challenge, we herein describe a reproducible protocol to generate human liver organoids in 20-25 days derived from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). These organoids are intra-luminally polarized to form canalicular structures and are comprised of mainly hepatic epithelial cells, co-differentiated with stellate-like and hepatic macrophage-like cells that enables hepatic inflammatory disease modeling in vitro. These multi-lineage liver organoids express hepatocyte genes, secrete albumin and have vital metabolic functions. This protocol utilizes PSC derived 3D human liver organoids as a renewable, reproducible and personalized cell source, thus facilitating disease modeling and mechanistic studies with a future goal of developing novel therapeutics against currently intractable diseases.
Keywords: Human liver organoids; Pluripotent stem cells; Self-organization; Steatohepatitis.
© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
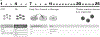
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

