Epidemic and pandemic viral infections: impact on tuberculosis and the lung: A consensus by the World Association for Infectious Diseases and Immunological Disorders (WAidid), Global Tuberculosis Network (GTN), and members of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Study Group for Mycobacterial Infections (ESGMYC)
- PMID: 32586885
- PMCID: PMC7527651
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.01727-2020
Epidemic and pandemic viral infections: impact on tuberculosis and the lung: A consensus by the World Association for Infectious Diseases and Immunological Disorders (WAidid), Global Tuberculosis Network (GTN), and members of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Study Group for Mycobacterial Infections (ESGMYC)
Abstract
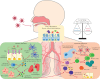
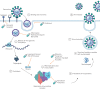
Major epidemics, including some that qualify as pandemics, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), HIV, influenza A (H1N1)pdm/09 and most recently COVID-19, affect the lung. Tuberculosis (TB) remains the top infectious disease killer, but apart from syndemic TB/HIV little is known regarding the interaction of viral epidemics and pandemics with TB. The aim of this consensus-based document is to describe the effects of viral infections resulting in epidemics and pandemics that affect the lung (MERS, SARS, HIV, influenza A (H1N1)pdm/09 and COVID-19) and their interactions with TB. A search of the scientific literature was performed. A writing committee of international experts including the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Public Health Emergency (ECDC PHE) team, the World Association for Infectious Diseases and Immunological Disorders (WAidid), the Global Tuberculosis Network (GTN), and members of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Study Group for Mycobacterial Infections (ESGMYC) was established. Consensus was achieved after multiple rounds of revisions between the writing committee and a larger expert group. A Delphi process involving the core group of authors (excluding the ECDC PHE team) identified the areas requiring review/consensus, followed by a second round to refine the definitive consensus elements. The epidemiology and immunology of these viral infections and their interactions with TB are discussed with implications for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of airborne infections (infection control, viral containment and workplace safety). This consensus document represents a rapid and comprehensive summary on what is known on the topic.
Copyright ©ERS 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: G.B. Migliori has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Raviglione has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: G. MacGregor-Skinner has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: G. Sotgiu has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J-W. Alffenaar has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Tiberi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Adlhoch has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T. Alonzi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Archuleta has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Brusin has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Cambau has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M.R. Capobianchi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Castilletti has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Centis has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D.M. Cirillo has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: L. D'Ambrosio has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: G. Delogu has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S.M.R. Esposito has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J. Figueroa has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J.S. Friedland has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: B.C.H. Ho has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: G. Ippolito has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Jankovic has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: H.Y. Kim has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Rosales Klintz has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Ködmön has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Lalle has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: Y.S. Leo has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C-C. Leung has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A-G. Märtson has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M.G. Melazzini has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Najafi Fard has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: P. Penttinen has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: L. Petrone has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Petruccioli has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: E. Pontali has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: L. Saderi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Santin has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Spanevello has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. van Crevel has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M.J. van der Werf has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D. Visca has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Viveiros has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J-P. Zellweger has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Zumla has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D. Goletti has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C.W.M. Ong has nothing to disclose.
Figures
Comment in
-
The impact of COVID-19 and the restoration of tuberculosis services in the Western Pacific Region.Eur Respir J. 2020 Oct 22;56(4):2003054. doi: 10.1183/13993003.03054-2020. Print 2020 Oct. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32978310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global tuberculosis report 2019. Geneva, WHO, 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
