Functional analysis of the OsNPF4.5 nitrate transporter reveals a conserved mycorrhizal pathway of nitrogen acquisition in plants
- PMID: 32586957
- PMCID: PMC7368293
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2000926117
Functional analysis of the OsNPF4.5 nitrate transporter reveals a conserved mycorrhizal pathway of nitrogen acquisition in plants
Abstract
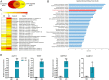
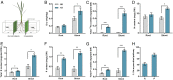
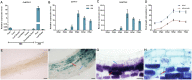
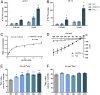
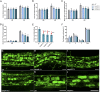
Low availability of nitrogen (N) is often a major limiting factor to crop yield in most nutrient-poor soils. Arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi are beneficial symbionts of most land plants that enhance plant nutrient uptake, particularly of phosphate. A growing number of reports point to the substantially increased N accumulation in many mycorrhizal plants; however, the contribution of AM symbiosis to plant N nutrition and the mechanisms underlying the AM-mediated N acquisition are still in the early stages of being understood. Here, we report that inoculation with AM fungus Rhizophagus irregularis remarkably promoted rice (Oryza sativa) growth and N acquisition, and about 42% of the overall N acquired by rice roots could be delivered via the symbiotic route under N-NO3- supply condition. Mycorrhizal colonization strongly induced expression of the putative nitrate transporter gene OsNPF4.5 in rice roots, and its orthologs ZmNPF4.5 in Zea mays and SbNPF4.5 in Sorghum bicolor OsNPF4.5 is exclusively expressed in the cells containing arbuscules and displayed a low-affinity NO3- transport activity when expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Moreover, knockout of OsNPF4.5 resulted in a 45% decrease in symbiotic N uptake and a significant reduction in arbuscule incidence when NO3- was supplied as an N source. Based on our results, we propose that the NPF4.5 plays a key role in mycorrhizal NO3- acquisition, a symbiotic N uptake route that might be highly conserved in gramineous species.
Keywords: OsNPF4.5; RNA sequencing; arbuscular mycorrhiza; nitrate transporter; nitrogen uptake.
Copyright © 2020 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Smith S. E., Smith F. A., Roles of arbuscular mycorrhizas in plant nutrition and growth: New paradigms from cellular to ecosystem scales. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 62, 227–250 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Gutjahr C., Parniske M., Cell and developmental biology of arbuscular mycorrhiza symbiosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 29, 593–617 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y. et al., Medicago AP2-domain transcription factor WRI5a is a master regulator of lipid biosynthesis and transfer during Mycorrhizal Symbiosis. Mol. Plant 11, 1344–1359 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Smith S. E., Smith F. A., Jakobsen I., Functional diversity in arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) symbioses: The contribution of the mycorrhizal P uptake pathway is not correlated with mycorrhizal responses in growth or total P uptake. New Phytol. 162, 511–524 (2003).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

