Anosmia in COVID-19 Associated with Injury to the Olfactory Bulbs Evident on MRI
- PMID: 32586960
- PMCID: PMC7583088
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A6675
Anosmia in COVID-19 Associated with Injury to the Olfactory Bulbs Evident on MRI
Abstract
Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may have symptoms of anosmia or partial loss of the sense of smell, often accompanied by changes in taste. We report 5 cases (3 with anosmia) of adult patients with COVID-19 in whom injury to the olfactory bulbs was interpreted as microbleeding or abnormal enhancement on MR imaging. The patients had persistent headache (n = 4) or motor deficits (n = 1). This olfactory bulb injury may be the mechanism by which the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 causes olfactory dysfunction.
© 2020 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures
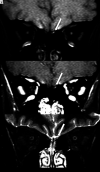
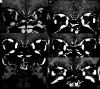
Comment in
-
Reply.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021 Jan;42(2):E2-E3. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6943. Epub 2020 Dec 3. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 33272952 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Seeing What We Expect to See in COVID-19.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021 Jan;42(2):E1. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6912. Epub 2020 Dec 3. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 33272953 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021 Sep;42(9):E66-E68. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7234. Epub 2021 Aug 5. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 34353782 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Susceptibility Artifacts in the Anterior Cranial Fossa Mimicking Hemorrhage in Patients with Anosmia.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021 Sep;42(9):E64-E65. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7184. Epub 2021 Aug 5. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 34353783 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fodoulian L, Tuberosa J, Rossier D, et al. . SARS-CoV-2 receptor and entry genes are expressed by sustentacular cells in the human olfactory neuroepithelium. bioRxiv 2020. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.31.013268v1. Accessed May 12, 2020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
