Painful trigeminal neuropathy associated with anti-Plexin D1 antibody
- PMID: 32587101
- PMCID: PMC7357409
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000819
Painful trigeminal neuropathy associated with anti-Plexin D1 antibody
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether anti-Plexin D1 antibody (Plexin D1-immunoglobulin G [IgG]), which is associated with limb and trunk neuropathic pain (NP) and binds to pain-conducting small unmyelinated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, exists in patients with idiopathic painful trigeminal neuropathy (IPTN) and whether Plexin D1-IgG binds to trigeminal ganglion (TG) neurons.
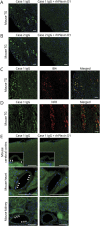
Methods: We enrolled 21 consecutive patients with IPTN and 35 age- and sex-matched controls without NP (25 healthy persons and 10 with neurodegenerative diseases). We measured serum Plexin D1-IgG using a mouse DRG tissue-based indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA) and by Western blotting (WB) using a recombinant human Plexin D1 (rhPlexin D1) accompanied by immunoadsorption tests with rhPlexin D1. The reactivity of Plexin D1-IgG toward mouse TG, brain, heart, and kidney was assessed by tissue-based IFAs.
Results: Serum Plexin D1-IgG was detected more frequently in IPTN than in controls by both IFA and WB (14.3% vs 0%, p = 0.048). Three Plexin D1-IgG-positive patients also had limb or trunk NP and commonly showed tongue pain. In tissue-based IFAs, IgG from 2 Plexin D1-IgG-positive patients immunostained small TG neurons, which was prevented by preincubation with rhPlexin D1. Moreover, Plexin D1-IgG immunostaining mostly colocalized with isolectin B4-positive pain-conducting unmyelinated TG neurons. IFAs of other tissues with the same IgG revealed weak immunoreactivity only in endothelial cells, which was prevented by preincubation with rhPlexin D1.
Conclusions: Plexin D1-IgG, which binds to pain-conducting small TG neurons in addition to DRG neurons, can be present in IPTN as well as limb and trunk NP.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Comment in
-
N2 in the time of COVID-19.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020 Aug 20;7(5):e858. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000000858. Print 2020 Sep. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020. PMID: 32820021 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018;38:1–211. - PubMed
-
- Fujii T, Yamasaki R, Iiunuma K, et al. A novel autoantibody against Plexin D1 in patients with neuropathic pain. Ann Neurol 2018;84:208–224. - PubMed
-
- Prineas JW, Parratt JDE. Multiple sclerosis: serum anti-CNS autoantibodies. Mult Scler 2018;24:610–622. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
