Post-cataract surgery cluster endophthalmitis due to multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A retrospective cohort study of six clusters
- PMID: 32587182
- PMCID: PMC7574127
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1612_19
Post-cataract surgery cluster endophthalmitis due to multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A retrospective cohort study of six clusters
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze clinical presentations, antibiotic susceptibility, and visual outcomes in six clusters of post cataract surgery endophthalmitis caused due to multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MDR-PA). This was a hospital-based retrospective cohort study.
Methods: Our study comprised sixty-two patients from six nonconsecutive clusters of post cataract surgery endophthalmitis caused by MDR-PA referred to our tertiary eye care institute. Demographic details, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA), clinical features, microbiological findings, and patient management were reviewed.
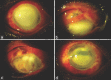
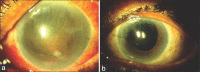
Results: The interval between onset of symptoms and presentation ranged from 1 to 7 (mean: 4.61 and median: 5) days. The presenting BCVA was no light perception in 17 (27.4%) eyes, light perception in 35 (56.4%) eyes, and hand movement or better in 10 (16.1%) eyes. All patients had hypopyon and vitreous exudates. Corneal infiltrates were noted in 40 (64.5%) eyes. Panophthalmitis was diagnosed in 20 (32.2%) eyes. The surgical intervention included intraocular antibiotics (IOAB) in 8 (12.9%) eyes, pars plana vitrectomy with IOAB in 26 (41.9%) eyes, and evisceration in 23 (37.09%) eyes. At 6 weeks, BCVA of 20/200 or better was achieved in 9 (14.5%) eyes. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was least resistant to colistin (8.3%), piperacillin (31.8%), and imipenem (36.1%). Ceftriaxone and ceftazidime resistance was seen in 80.5% and 70% isolates, respectively.
Conclusion: Cluster endophthalmitis due to MDR-PA has poor visual outcomes with high rates of evisceration. In the setting of cluster endophthalmitis where MDR-PA is the most common etiology, piperacillin or imipenem can be the first drug of choice for empirical intravitreal injection for gram-negative coverage while awaiting the drug susceptibility report.
Keywords: Antibiotics resistance; cataract surgery; cluster endophthalmitis; endophthalmitis; multidrug-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa; pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Ramappa M, Majji AB, Murthy SI, Balne PK, Nalamada S, Garudadri C, et al. An outbreak of acute post-cataract surgery Pseudomonas sp. Endophthalmitis caused by contaminated hydrophilic intraocular lens solution. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:564–70. - PubMed
-
- Pinna A, Usai D, Sechi LA, Zanetti S, Jesudasan NC, Thomas PA, et al. An outbreak of post-cataract surgery endophthalmitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ophthalmology. 2009;116:2321–6. - PubMed
-
- Pathengay A, Flynn H, Jr, Isom R, Miller D. Endophthalmitis outbreaks following cataract surgery: Causative organisms, etiologies and visual acuity outcomes. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38:1278–82. - PubMed
-
- Kresloff MS, Castellarin AA, Zarbin MA. Endophthalmitis. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998;43:193–224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

