Unique Genetic Characteristics and Clinical Prognosis of Female Patients with Lung Cancer Harboring RET Fusion Gene
- PMID: 32587276
- PMCID: PMC7316706
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-66883-0
Unique Genetic Characteristics and Clinical Prognosis of Female Patients with Lung Cancer Harboring RET Fusion Gene
Abstract
Objectives: Since no report on the genetic characteristics of RET fusions in female patients with lung cancer is available, this study revealed the genetic and prognostic characteristics of female patients with lung cancer harboring RET fusion gene for the first time.
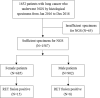
Materials and methods: The molecular portfolios of 1,652 patients with lung cancer who underwent targeted next-generation sequencing for screening candidate oncogenic drivers in their histological specimens from January 2016 to December 2018 were investigated in this study.
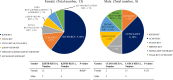
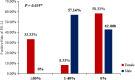
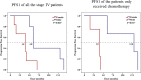
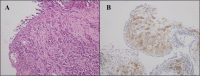
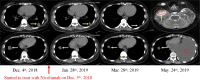
Results: RET fusions were identified in 23 cases, 15 females [2.2% (15/685)] and eight males [0.9% (8/902)]. The most common fusions were KIF5B-RET in females [80% (12/15)] and CCDC6-RET in males [50% (4/8)], along with some rare RET fusions, including SLC39A8-RET, ITIH2-RET, FYCO1-RET and SLC25A36-RET in females, and MIR3924-RET, ZBTB41-RET and ITGA8-RET in males. Interestingly, the highly positive, moderate positive, and negative rates of PD-L1 staining in females were 33.3%, 8.3% and 58.3%, respectively; whereas those in males were 0%, 57.1% and 42.9%. Additionally, the progression-free survival (PFS) of stage IV patients was comparatively shorter in females, shown by the medians of 4.0 months in females and 6.0 months in males (P = 0.029). A 43-year-old female patient with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma, who harbored KIF5B-RET fusion and had highly positive PD-L1 staining, received nivolumab as second-line treatment. A partial response was achieved and remained for more than five months.
Conclusion: Unique genetic characteristics and poor prognosis are found in female patients with lung cancer harboring RET fusion gene. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are a potential option for patients with high expression of PD-L1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association Between RET Fusions and Efficacy of Pemetrexed-based Chemotherapy for Patients With Advanced NSCLC in China: A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Clin Lung Cancer. 2020 Sep;21(5):e349-e354. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.02.006. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Clin Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32143967
-
Characteristics and outcomes of patients with RET-fusion positive non-small lung cancer in real-world practice in the United States.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jan 5;21(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07714-3. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33402119 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of incorporating next-generation sequencing (NGS) in an Asian non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) population: Incremental yield of actionable alterations and cost-effectiveness analysis.Lung Cancer. 2020 Jan;139:207-215. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.11.022. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31835042
-
[The progress of KIF5B-RET fusion gene in non-small cell lung cancer].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013 Jul;36(7):524-6. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24262090 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Therapeutic Advances in the Management of Patients with Advanced RET Fusion-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021 Jun 24;22(8):72. doi: 10.1007/s11864-021-00867-8. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34165651 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural investigations, quantum mechanical studies on proton and metal affinity and biological activity predictions of selpercatinib.J Mol Liq. 2021 Mar 1;325:114765. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114765. Epub 2020 Nov 13. J Mol Liq. 2021. PMID: 33746318 Free PMC article.
-
Current Targeted Therapies for the Fight against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Nov 9;13(11):374. doi: 10.3390/ph13110374. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33182254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with RET Fusions: Reality and Hopes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 26;24(3):2433. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032433. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RET Fusion Testing in Patients With NSCLC: The RETING Study.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2024 Feb 20;5(4):100653. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2024.100653. eCollection 2024 Apr. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2024. PMID: 38525319 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of CCDC6 in relation to unfavorable outcome and immune cells infiltration in hepatobiliary carcinoma.J Cancer. 2022 Sep 21;13(12):3378-3395. doi: 10.7150/jca.76050. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36186907 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

