Methylation Patterns of the HTR2A Associate With Relapse-Related Behaviors in Cocaine-Dependent Participants
- PMID: 32587535
- PMCID: PMC7299072
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00532
Methylation Patterns of the HTR2A Associate With Relapse-Related Behaviors in Cocaine-Dependent Participants
Abstract
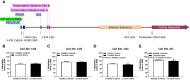
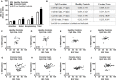
Relapse during abstinence in cocaine use disorder (CUD) is often hastened by high impulsivity (predisposition toward rapid unplanned reactions to stimuli without regard to negative consequences) and high cue reactivity (e.g., attentional bias towards drug reward stimuli). A deeper understanding of the degree to which individual biological differences predict or promote problematic behaviors may afford opportunities for clinical refinement and optimization of CUD diagnostics and/or therapies. Preclinical evidence implicates serotonin (5-HT) neurotransmission through the 5-HT2A receptor (5-HT2AR) as a driver of individual differences in these relapse-related behaviors. Regulation of 5-HT2AR function occurs through many mechanisms, including DNA methylation of the HTR2A gene, an epigenetic modification linked with the memory of gene-environment interactions. In the present study, we tested the hypothesis that methylation of the HTR2A may associate with relapse-related behavioral vulnerability in cocaine-dependent participants versus healthy controls. Impulsivity was assessed by self-report (Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BIS-11) and the delay discounting task, while levels of cue reactivity were determined by performance in the cocaine-word Stroop task. Genomic DNA was extracted from lymphocytes and the bisulfite-treated DNA was subjected to pyrosequencing to determine degree of methylation at four cytosine residues of the HTR2A promoter (-1439, -1420, -1224, -253). We found that the percent methylation at site -1224 after correction for age trended towards a positive correlation with total BIS-11 scores in cocaine users, but not healthy controls. Percent methylation at site -1420 negatively correlated with rates of delay discounting in healthy controls, but not cocaine users. Lastly, the percent methylation at site -253 positively correlated with attentional bias toward cocaine-associated cues. DNA methylation at these cytosine residues of the HTR2A promoter may be differentially associated with impulsivity or cocaine-associated environmental cues. Taken together, these data suggest that methylation of the HTR2A may contribute to individual differences in relapse-related behaviors in CUD.
Keywords: A-1438G; HTR2A; attentional bias; cocaine use disorder; impulsivity; methylation; rs6311.
Copyright © 2020 Land, Ramesh, Miller, Pyles, Cunningham, Moeller and Anastasio.
Figures

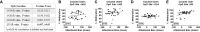
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

