High Light-Induced Nitric Oxide Production Induces Autophagy and Cell Death in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 32587598
- PMCID: PMC7298128
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00772
High Light-Induced Nitric Oxide Production Induces Autophagy and Cell Death in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
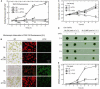
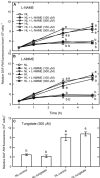
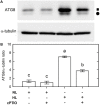
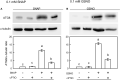
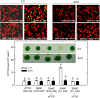
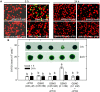
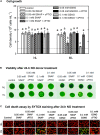
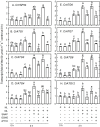
Autophagy plays a role in regulating important cellular functions in response to stress conditions. The role of nitric oxide (NO) in the regulation of autophagy in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has been not studied. Illumination of C. reinhardtii cells under a high light (HL, 1,600 μmol m-2 s-1) condition induced a NO burst through NO synthase- and nitrate reductase-independent routes, and cell death. The abundance of CrATG8 protein, an autophagy marker of C. reinhardtii, increased after HL illumination along with a linear increase in the transcript abundance of autophagy-associated genes (CrVPS34, CrATG1, CrATG3, CrATG4, CrATG6, CrATG7, CrATG8, and CrATG12), which were suppressed in the presence of an NO scavenger, 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxyl-3-oxide (cPTIO). The cells were treated with NO donors, S-nitroso-N-acetyl-penicillamine, and S-nitrosoglutathione, under a normal light (50 μmol m-2 s-1) condition to elucidate the role of NO in autophagy activation and cell death. Treatment with 0.05 mM or 0.1 mM NO donors increased the abundance of ATG8 protein and CrATG transcripts, which were suppressed in the presence of cPTIO. Moreover, treatment with 0.05 mM NO donors did not affect cell viability, while 0.1 mM NO donors elicited a transient decrease in cell growth and death that recovered after 12 h. The transient effect could be prevented by the presence of cPTIO. However, treatment with 1 mM H2O2 and 0.1 mM NO donors enhanced autophagy induction and resulted in cell death after 24 h. The interaction of H2O2 and NO can be prevented by cPTIO treatment. This implies that NO is critical for the interaction of H2O2 and NO that induces cell death and autophagy. Furthermore, exposure to 0.1 mM NO donors under a non-lethal HL condition (750 μmol m-2 s-1) evoked autophagy and cell death. In conclusion, the present findings demonstrated that the NO-mediated autophagy pathway is activated in C. reinhardtii under lethal high intensity illumination and may interact with H2O2 for HL-induced cell death. The relationships between autophagy and cell death are discussed.
Keywords: Chlamydomonas; autophagy; autophagy-related protein; cell death; high light; nitric oxide.
Copyright © 2020 Kuo, Chang, Lin and Lee.
Figures






References
-
- Arasimowicza M., Floryszak-Wieczorek J. (2007). Nitric oxide as a bioactive signalling molecule in plant stress responses. Plant Sci. 172 876–887. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.02.005 - DOI
-
- Bajguz A. (2014). “Nitric oxide: role in plants under abiotic stress,” in Physiological Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies in Plants Under Changing Environments, eds Ahmad R., Wani M. R. (New York, NY: Springer; ), 137–160.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

