Neurological features of COVID-19 and their treatment: a review
- PMID: 32587625
- PMCID: PMC7295105
- DOI: 10.7573/dic.2020-5-1
Neurological features of COVID-19 and their treatment: a review
Abstract
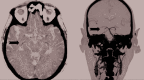
Severe acute respiratory syndrome-correlated new coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) infection may result in neurological signs and symptoms through different mechanisms. Although direct infection of the central nervous system is uncertain or very rare and the para-infectious complications (e.g. inflammatory neuropathies) are rare, delirium and septic encephalopathy are common in severely ill patients. Smell dysfunction and headache are very common in mild cases, especially in younger people and females. Muscle pain is common in both mild and severe cases, and in the most compromised patients, it is accompanied by increased creatine kinase levels and by a likely true myopathic damage. Ischemic stroke has been reported as a possible complication of the hypercoagulability associated with severe SARS-Cov-2 infection, but further studies are needed. Most of the neurological manifestations may occur early in the illness. Therefore, during the pandemic period, neurologists need to be involved, alert, and prepared. Neurological practice will not be the same until a vaccine is available.
Keywords: COVID-19; CPK; Guillain-Barré syndrome; Sars-Cov-2; anosmia; coronavirus; myopathy; myositis; stroke.
Copyright © 2020 Orsucci D, Caldarazzo Ienco E, Nocita G, Napolitano A, Vista M.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and potential conflicts of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) Potential Conflicts of Interests form for the authors is available for download at: https://www.drugsincontext.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/dic.2020-5-1-COI.pdf
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

