Rutin via Increase in the CA3 Diameter of the Hippocampus Exerted Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mouse Model of Maternal Separation Stress: Possible Involvement of NMDA Receptors
- PMID: 32587637
- PMCID: PMC7296444
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4813616
Rutin via Increase in the CA3 Diameter of the Hippocampus Exerted Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mouse Model of Maternal Separation Stress: Possible Involvement of NMDA Receptors
Abstract
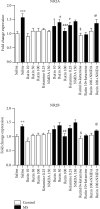
Methods: Mouse neonates were exposed to MS paradigm 3 hours daily from postnatal days (PND) 2 to 14. The control and MS mice were divided separately into 16 groups (n = 8) (8 groups for each set) including mice that received normal saline, mice that received rutin at doses of 10, 50, and 100 mg/kg, mice that received NMDA at a dose of 150 mg/kg, mice that received ketamine (NMDA antagonist) at a dose of 0.25 mg/kg, mice that received NMDA antagonist plus a subeffective dose of rutin, and mice that received NMDA plus an effective dose of rutin. Forced swimming test (FST) was performed. Afterwards, the hippocampus was evaluated in cases of histopathological changes as well as expression of NR2A and NR2B genes.
Results: Rutin significantly reduced immobility time in the FST. The expression of NR2A and NR2B subunits of NMDA receptor in MS mice was significantly higher than that in the control group. Rutin significantly decreased the expression of NR2B and NR2A subunits in the hippocampus. The CA3 diameter and percentage of dark neurons in the hippocampus of MS mice significantly decreased and increased, respectively, which partially reversed following rutin administration.
Conclusion: Rutin, partially, through a neuroprotective effect on the hippocampus exerted antidepressant-like effect. We concluded that NMDA receptors, at least in part, mediated the beneficial effect of rutin.
Copyright © 2020 Maryam Anjomshoa et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare regarding the study described in this article and preparation of the article.
Figures





References
-
- Jazayeri S., Keshavarz S. A., Tehrani-Doost M., et al. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and fluoxetine on plasma cortisol, serum interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6 concentrations in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychiatry Research. 2010;178(1):112–115. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2009.04.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Emamghoreishi M., Talebianpour M. Antidepressant effect of Melissa officinalis in the forced swimming test. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2015;17(1):42–47.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

