CDK11 negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the endosomal compartment by affecting microtubule stability
- PMID: 32587772
- PMCID: PMC7309457
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0229
CDK11 negatively regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the endosomal compartment by affecting microtubule stability
Abstract
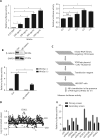
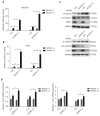
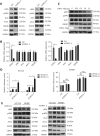
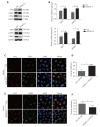
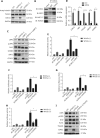
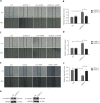
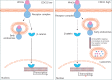
Objectives: Improper activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling has been implicated in human diseases. Beyond the well-studied glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) and casein kinase 1 (CK1), other kinases affecting Wnt/β-catenin signaling remain to be defined. Methods:To identify the kinases that modulate Wnt/β-catenin signaling, we applied a kinase small interfering RNA (siRNA) library screen approach. Luciferase assays, immunoblotting, and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) were performed to confirm the regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by cyclin-dependent kinase 11 (CDK11) and to investigate the underlying mechanism. Confocal immunofluorescence, coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP), and scratch wound assays were used to demonstrate colocalization, detect protein interactions, and explore the function of CDK11. Results: CDK11 was found to be a significant candidate kinase participating in the negative control of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Down-regulation of CDK11 led to the accumulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling receptor complexes, in a manner dependent on intact adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC) protein. Further analysis showed that CDK11 modulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling engaged the endolysosomal machinery, and CDK11 knockdown enhanced the colocalization of Wnt/β-catenin signaling receptor complexes with early endosomes and decreased colocalization with lysosomes. Mechanistically, CDK11 was found to function in Wnt/β-catenin signaling by regulating microtubule stability. Depletion of CDK11 down-regulated acetyl-α-tubulin. Moreover, co-IP assays demonstrated that CDK11 interacts with the α-tubulin deacetylase SIRT2, whereas SIRT2 down-regulation in CDK11-depleted cells reversed the accumulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling receptor complexes. CDK11 was found to suppress cell migration through altered Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Conclusions: CDK11 is a negative modulator of Wnt/β-catenin signaling that stabilizes microtubules, thus resulting in the dysregulation of receptor complex trafficking from early endosomes to lysosomes.
Keywords: CDK11; SIRT2; Wnt/β-catenin signaling; endosome; microtubule.
Copyright: © 2020, Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–80. - PubMed
-
- Polakis P. The many ways of Wnt in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Anastas JN, Moon RT. Wnt signalling pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:11–26. - PubMed
-
- Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY, Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, et al. Wnt signaling through inhibition of beta-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell. 2012;149:1245–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
