Identification and Validation of a Prognostic lncRNA Signature for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32587825
- PMCID: PMC7298074
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00780
Identification and Validation of a Prognostic lncRNA Signature for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
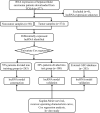
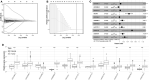
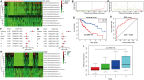
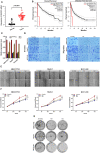
Background: An accumulating body of evidence suggests that long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) can serve as potential cancer prognostic factors. However, the utility of lncRNA combinations in estimating overall survival (OS) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains to be elucidated. This study aimed to construct a powerful lncRNA signature related to the OS for HCC to enhance prognostic accuracy. Methods: The expression patterns of lncRNAs and related clinical data of 371 HCC patients were obtained based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) were acquired by comparing tumors with adjacent normal samples. lncRNAs displaying significant association with OS were screened through univariate Cox regression analysis and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) algorithm. All cases were classified into the validation or training group at the ratio of 3:7 to validate the constructed lncRNA signature. Data from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) were used for external validation. We conducted real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and assays for Transwell invasion, migration, CCK-8, and colony formation to determine the biological roles of lncRNA. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of the lncRNA model risk score was also conducted. Results: We identified 1292 DElncRNAs, among which 172 were significant in univariate Cox regression analysis. In the training group (n = 263), LASSO regression analysis confirmed 11 DElncRNAs including AC010547.1, AC010280.2, AC015712.7, GACAT3 (gastric cancer associated transcript 3), AC079466.1, AC089983.1, AC051618.1, AL121721.1, LINC01747, LINC01517, and AC008750.3. The prognostic risk score was calculated, and the constructed risk model showed significant correlation with HCC OS (log-rank P-value of 8.489e-9, hazard ratio of 3.648, 95% confidence interval: 2.238-5.945). The area under the curve (AUC) for this lncRNA model was up to 0.846. This risk model was confirmed in the validation group (n = 108), the entire cohort, and the external GEO dataset (n = 203). GACAT3 was highly expressed in HCC tissues and cell lines. Based on online databases, GACAT3 expression independently affects both OS and disease-free survival in HCC patients. Silencing GACAT3 in vitro significantly suppressed HCC cell proliferation, invasion, and migration. Moreover, pathways related to the lncRNA model risk score were confirmed by GSEA. Conclusion: The lncRNA signature established in this study can be used to predict HCC prognosis, which could provide novel clinical evidence to guide targeted HCC treatment.
Keywords: TCGA; hepatocellular carcinoma; least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; long non-coding RNAs; prognosis analysis.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Chen, Huang, Wu, Shen and Huang.
Figures



References
-
- Chen QF, Jia ZY, Yang ZQ, Fan WL, Shi HB. Transarterial chemoembolization monotherapy versus combined transarterial chemoembolization-microwave ablation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma tumors </=5 cm: a propensity analysis at a single center. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. (2017) 40:1748–55. 10.1007/s00270-017-1736-8 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

