RcsAB and Fur Coregulate the Iron-Acquisition System via entC in Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044 in Response to Iron Availability
- PMID: 32587833
- PMCID: PMC7298118
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00282
RcsAB and Fur Coregulate the Iron-Acquisition System via entC in Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044 in Response to Iron Availability
Abstract
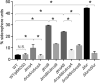
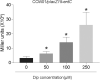
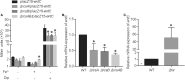
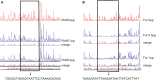
The iron acquisition system is an essential virulence factor for human infection and is under tight regulatory control in a variety of pathogens. Ferric-uptake regulator (Fur) is one of Fe2+-responsive transcription factor that maintains iron homeostasis, and the regulator of capsule synthesis (Rcs) is known to regulate exopolysaccharide biosynthesis. We speculate the Rcs may involve in iron-acquisition given the identified regulator box in the upstream of entC that participated in the biosynthesis of enterobactin. To study the coregulation by RcsAB and Fur of entC, we measured the β-galactosidase activity and relative mRNA expression of entC in WT and mutant strains. The RcsAB- and Fur-protected regions were identified by an electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and a DNase I footprinting assay. A regulatory cascade was identified with which Fur repressed rcsA expression and reduced RcsAB and entC expression. Our study demonstrated that entC was coregulated by two different transcriptional regulators, namely, RcsAB and Fur, in response to iron availability in Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Keywords: Fur; Klebsiella pneumoniae; RcsAB; entC; iron-acquisition system.
Copyright © 2020 Yuan, Li, Du, Su, Zhang, Liu, He, Zhang, Peng, Shen, Qiu and Li.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation of the yersiniabactin receptor fyuA gene by the ferric uptake regulator in Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044.J Basic Microbiol. 2024 Aug;64(8):e2400001. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202400001. Epub 2024 Apr 28. J Basic Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38679904
-
Transcriptional regulation of galF by RcsAB affects capsular polysaccharide formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044.Microbiol Res. 2018 Nov;216:70-78. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 25. Microbiol Res. 2018. PMID: 30269858
-
Regulation of ECP fimbriae-related genes by the transcriptional regulator RcsAB in Klebsiella pneumoniae NTUH-K2044.J Basic Microbiol. 2022 May;62(5):593-603. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202100595. Epub 2022 Feb 8. J Basic Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35132658
-
Interplay between iron homeostasis and virulence: Fur and RyhB as major regulators of bacterial pathogenicity.Vet Microbiol. 2015 Aug 31;179(1-2):2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.03.024. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Vet Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25888312 Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation by Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) in pathogenic bacteria.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013 Oct 2;3:59. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2013.00059. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24106689 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic Investigation of Intestinal Microbiota of Insectivorous Synanthropic Bats: Densoviruses, Antibiotic Resistance Genes, and Functional Profiling of Gut Microbial Communities.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 20;26(13):5941. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135941. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649719 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based analyses of Salmonella RcsB variants unravel new features of the Rcs regulon.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Feb 26;49(4):2357-2374. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab060. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33638994 Free PMC article.
-
First whole genome report of Mangrovibacter phragmitis PSU-3885-11 isolated from a patient in Thailand.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2025 Jan 22;8:100350. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2025.100350. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2025. PMID: 39911356 Free PMC article.
-
Capsular Polysaccharide as a Potential Target in Hypervirulent and Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Treatment.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 3;18:1253-1262. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S493635. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40059940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metagenome Analysis of the Bacterial Characteristics in Invasive Klebsiella Pneumoniae Liver Abscesses.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 15;12:812542. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.812542. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35909970 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

