Dual-Targeting Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Therapy Strategy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Delivering Small Interfering RNA
- PMID: 32587849
- PMCID: PMC7297947
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00512
Dual-Targeting Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Therapy Strategy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Delivering Small Interfering RNA
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Dual-Targeting Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Therapy Strategy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Delivering Small Interfering RNA.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Feb 11;9:656268. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.656268. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33644028 Free PMC article.
Abstract
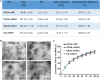
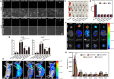
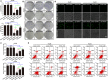
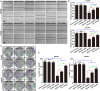
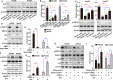
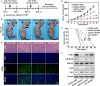
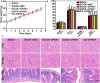
As a gene therapy strategy, RNA interference (RNAi) offers tremendous tumor therapy potential. However, its therapeutic efficacy is restricted by its inferior ability for targeted delivery and cellular uptake of small interfering RNA (siRNA). This study sought to develop a dual-ligand nanoparticle (NP) system loaded with siRNA to promote targeted delivery and therapeutic efficacy. We synthesized a dual receptor-targeted chitosan nanosystem (GCGA), whose target function was controlled by the ligands of galactose of lactobionic acid (LA) and glycyrrhetinic acid (GA). By loading siPAK1, an siRNA targeting P21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1), a molecular-targeted therapeutic dual-ligand NP (GCGA-siPAK1) was established. We investigated the synergistic effect of these two targeting units in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In particular, GCGA-siPAK1 enhanced the NP targeting ability and promoted siPAK1 cell uptake. Subsequently, dramatic decreases in cell proliferation, invasion, and migration, with an apparent increase in cell apoptosis, were observed in treated cells. Furthermore, this dual-ligand NP gene delivery system demonstrated significant anti-tumor effects in tumor-bearing mice. Finally, we illuminated the molecular mechanism, whereby GCGA-siPAK1 promotes endogenous cell apoptosis through the PAK1/MEK/ERK pathway. Thus, the dual-target property effectively promotes the HCC therapeutic effect and provides a promising gene therapy strategy for clinical applications.
Keywords: chitosan; drug delivery; gene therapy; hepatocellular carcinoma; small interfering RNA; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2020 Zheng, Jiang, Wu, Shang, Zhang, Hu, Cheng, Zhang, Sun, Gao, Song and Li.
Figures




References
-
- Cheng A. L., Kang Y. K., Chen Z. D., Tsao C. J., Qin S. K., Kim J. S., et al. . (2009). Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10, 25–34. 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70285-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

