Toxicity Evaluation of TiO2 Nanoparticles on the 3D Skin Model: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 32587852
- PMCID: PMC7298140
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00575
Toxicity Evaluation of TiO2 Nanoparticles on the 3D Skin Model: A Systematic Review
Abstract
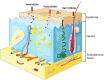
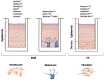
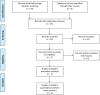
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) are regularly used in sunscreens because of their photoprotective capacity. The advantage of using TiO2 on the nanometer scale is due to its transparency and better UV blocking efficiency. Due to the greater surface area/volume ratio, NPs become more (bio)-reactive giving rise to concerns about their potential toxicity. To evaluate the irritation and corrosion of cosmetics, 3D skin models have been used as an alternative method to animal experimentation. However, it is not known if this model is appropriate to study skin irritation, corrosion and phototoxicity of nanomaterials such as TiO2 NPs. This systematic review (SR) proposed the following question: Can the toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles be evaluated in a 3D skin model? This SR was conducted according to the Preliminary Report on Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA). The protocol was registered in CAMARADES and the ToxRTool evaluation was performed in order to increase the quality and transparency of this search. In this SR, 7 articles were selected, and it was concluded that the 3D skin model has shown to be promising to evaluate the toxicity of TiO2 NPs. However, most studies have used biological assays that have already been described as interfering with these NPs, demonstrating that misinterpretations can be obtained. This review will focus in the possible efforts that should be done in order to avoid interference of NPs with biological assays applied in 3D in vitro culture.
Keywords: 3D skin model; alternative method; nanoparticles; titanium dioxide; toxicity.
Copyright © 2020 Sanches, Geaquinto, Cruz, Schuck, Lorencini, Granjeiro and Ribeiro.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

