Relationships between big-five personality factors and Alzheimer's disease pathology in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 32587883
- PMCID: PMC7311802
- DOI: 10.1002/dad2.12038
Relationships between big-five personality factors and Alzheimer's disease pathology in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Changes in personality characteristics are associated with the onset of symptoms in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and may even precede clinical diagnosis. However, personality changes caused by disease progression can be difficult to separate from changes that occur with normal aging. The Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN) provides a unique cohort in which to relate measures of personality traits to in vivo markers of disease in a much younger sample than in typical late onset AD.
Methods: Personality traits measured with the International Personality Item Pool at baseline from DIAN participants were analyzed as a function of estimated years to onset of clinical symptoms and well-established AD biomarkers.
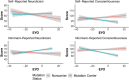
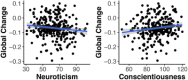
Results: Both neuroticism and conscientiousness were correlated with years to symptom onset and markers of tau pathology in the cerebrospinal fluid. Self-reported conscientiousness and both neuroticism and conscientiousness ratings from a collateral source were correlated with longitudinal rates of cognitive decline such that participants who were rated as higher on neuroticism and lower on conscientiousness exhibited accelerated rates of cognitive decline.
Discussion: Personality traits are correlated with the accumulation of AD pathology and time to symptom onset, suggesting that AD progression can influence an individual's personality characteristics. Together these findings suggest that measuring neuroticism and conscientiousness may hold utility in tracking disease progression in AD.
© 2020 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Alison Goate served on the scientific advisory board for Denali Therapeutics from 2015 to 2018. She has also served as a consultant for Biogen, AbbVie, Pfizer, GSK, Eisai, and Illumina. Dr. Benzinger reports grants, non‐financial support, and clinical trial participation involving Avid Radiopharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly. She serves as an investigator in clinical trials sponsored by Roche, Biogen, Jaansen, and Eisai. She reports unpaid consulting: Siemens, Eisai, ADMDx. She is on the Biogen speakers’ bureau. All of this is outside the scope of the current manuscript. Dr. Neil Graff‐Radford takes part in multicenter treatment trials funded by Novartis, AbbVie, Biogen, and Lilly. Dr. JC Morris is funded by NIH grants # P50AG005681, P01AG003991, P01AG026276, and UF1AG032438. Neither Dr. Morris nor his family owns stock or has equity interest (outside of mutual funds or other externally directed accounts) in any pharmaceutical or biotechnology company. No other conflicts are reported.
Figures

References
-
- McCrae RR, John OP. An introduction to the five‐factor model and its applications. J Pers. 1992;60(2):175‐215. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
