RNA from stabilized whole blood enables more comprehensive immune gene expression profiling compared to RNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 32589655
- PMCID: PMC7319339
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235413
RNA from stabilized whole blood enables more comprehensive immune gene expression profiling compared to RNA from peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
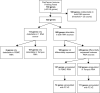
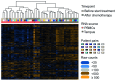
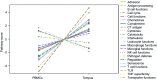
Monitoring changes in the immune profile in blood samples can help identifying changes in tumor biology and therapy responsiveness over time. Immune-related gene expression profiles offer a highly reproducible method to monitor changes of the immune system. However, measuring gene expression profiles in whole blood samples can be complicated because of the high protein and enzyme abundancy that affect the stability and quality of the RNA. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) are one the most commonly used source for immune cell RNA extraction, though, this method does not reflect all components of the peripheral blood. The aim of this study was to determine the differences in immune-related gene expression between RNA isolated from stabilized whole blood and RNA isolated from PBMCs. Whole blood samples from 12 pancreatic cancer patients were collected before and after chemotherapy (n = 24). Blood samples were collected in both EDTA tubes, and Tempus tubes containing an RNA stabilizer (total n = 48). PBMCs were isolated from EDTA samples using Ficoll and were snap frozen. Subsequently, immune-related gene expression was profiled using the PanCancer Immune Profiling Panel of NanoString technology. Gene expression profiles of PBMCs were compared to that of Tempus tubes using the Advanced Analysis module of nSolver software. Both types of samples provided good quality RNA and gene expression measurements. However, RNA isolated from Tempus tubes resulted in significantly higher gene counts than PBMCs; 107/730 genes were exclusively detected in Tempus samples, while under the detection limit in PBMCs. In addition, 192/730 genes showed significantly higher gene counts in Tempus samples, 157/730 genes showed higher gene counts in PBMCs. Thus, RNA isolated from whole blood stabilizing blood tubes, such as Tempus tubes, enable higher gene counts and more comprehensive measurements of gene expression profiles compared to RNA isolated from PBMCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigating gene expression profiles of whole blood and peripheral blood mononuclear cells using multiple collection and processing methods.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 6;14(12):e0225137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225137. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31809517 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression profiles are dependent upon method of peripheral blood collection and RNA isolation.BMC Genomics. 2008 Oct 10;9:474. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-474. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18847473 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression differences between PAXgene and Tempus blood RNA tubes are highly reproducible between independent samples and biobanks.BMC Res Notes. 2017 Mar 23;10(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2455-6. BMC Res Notes. 2017. PMID: 28335817 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of blood collection and processing on peripheral blood gene expression profiling in type 1 diabetes.BMC Genomics. 2017 Aug 18;18(1):636. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3949-2. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28821222 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells.In: Verhoeckx K, Cotter P, López-Expósito I, Kleiveland C, Lea T, Mackie A, Requena T, Swiatecka D, Wichers H, editors. The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: in vitro and ex vivo models [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2015. Chapter 15. In: Verhoeckx K, Cotter P, López-Expósito I, Kleiveland C, Lea T, Mackie A, Requena T, Swiatecka D, Wichers H, editors. The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: in vitro and ex vivo models [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2015. Chapter 15. PMID: 29787062 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Transmissible cancer influences immune gene expression in an endangered marsupial, the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii).Mol Ecol. 2022 Apr;31(8):2293-2311. doi: 10.1111/mec.16408. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Mol Ecol. 2022. PMID: 35202488 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized protocol for the extraction of RNA and DNA from frozen whole blood sample stored in a single EDTA tube.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 23;11(1):17075. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96567-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34426633 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-COV-2 causes significant abnormalities in the fibrinolysis system of patients: correlation between viral mutations, variants and thrombosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 15;15:1531412. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1531412. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40302923 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of SIRT1/FOXO1 Signaling Pathway in Early Detection of Cardiovascular Risk in Children with β-Thalassemia Major.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 17;10(10):2601. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102601. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289866 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct CholinomiR Blood Cell Signature as a Potential Modulator of the Cholinergic System in Women with Fibromyalgia Syndrome.Cells. 2022 Apr 9;11(8):1276. doi: 10.3390/cells11081276. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455956 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

