Synergistic targeting of FLT3 mutations in AML via combined menin-MLL and FLT3 inhibition
- PMID: 32589720
- PMCID: PMC8215191
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2020005037
Synergistic targeting of FLT3 mutations in AML via combined menin-MLL and FLT3 inhibition
Abstract
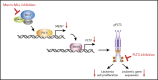
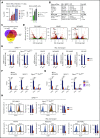
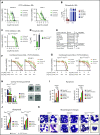
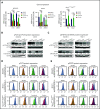
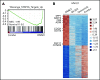
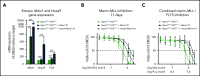
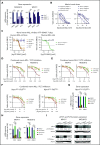
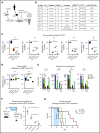
The interaction of menin (MEN1) and MLL (MLL1, KMT2A) is a dependency and provides a potential opportunity for treatment of NPM1-mutant (NPM1mut) and MLL-rearranged (MLL-r) leukemias. Concomitant activating driver mutations in the gene encoding the tyrosine kinase FLT3 occur in both leukemias and are particularly common in the NPM1mut subtype. In this study, transcriptional profiling after pharmacological inhibition of the menin-MLL complex revealed specific changes in gene expression, with downregulation of the MEIS1 transcription factor and its transcriptional target gene FLT3 being the most pronounced. Combining menin-MLL inhibition with specific small-molecule kinase inhibitors of FLT3 phosphorylation resulted in a significantly superior reduction of phosphorylated FLT3 and transcriptional suppression of genes downstream of FLT3 signaling. The drug combination induced synergistic inhibition of proliferation, as well as enhanced apoptosis, compared with single-drug treatment in models of human and murine NPM1mut and MLL-r leukemias harboring an FLT3 mutation. Primary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells harvested from patients with NPM1mutFLT3mut AML showed significantly better responses to combined menin and FLT3 inhibition than to single-drug or vehicle control treatment, whereas AML cells with wild-type NPM1, MLL, and FLT3 were not affected by either of the 2 drugs. In vivo treatment of leukemic animals with MLL-r FLT3mut leukemia reduced leukemia burden significantly and prolonged survival compared with results in the single-drug and vehicle control groups. Our data suggest that combined menin-MLL and FLT3 inhibition represents a novel and promising therapeutic strategy for patients with NPM1mut or MLL-r leukemia and concurrent FLT3 mutation.
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: M.W.M.K, is a consultant for Pfizer and Abbvie and receives travel support from Celgene and Daiichi Sankyo. S.A.A. is a consultant and/or shareholder for Epizyme Inc, Vitae/Allergan Pharmaceuticals, Imago Biosciences, Cyteir Therapeutics, C4 Therapeutics, Syros Pharmaceuticals, OxStem Oncology, Accent Therapeutics, and Mana Therapeutics and has received research support from Janssen, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. G.S.V. is a consultant for Kymab and Oxstem. G.M.M. is a shareholder of Syndax Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
MLL-menin and FLT3 inhibitors team up for AML.Blood. 2020 Nov 19;136(21):2369-2370. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007671. Blood. 2020. PMID: 33211832 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Targeting Chromatin Regulators Inhibits Leukemogenic Gene Expression in NPM1 Mutant Leukemia.Cancer Discov. 2016 Oct;6(10):1166-1181. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0237. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 27535106 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical efficacy of the potent, selective menin-KMT2A inhibitor JNJ-75276617 (bleximenib) in KMT2A- and NPM1-altered leukemias.Blood. 2024 Sep 12;144(11):1206-1220. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023022480. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38905635 Free PMC article.
-
Co-inhibition of HDAC and MLL-menin interaction targets MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia cells via disruption of DNA damage checkpoint and DNA repair.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Oct 7;11(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0723-0. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 31590682 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with aberrant HOX/MEIS1 expression.Eur J Med Genet. 2023 Dec;66(12):104869. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2023.104869. Epub 2023 Oct 29. Eur J Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 38174649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives for therapeutic targeting of gene mutations in acute myeloid leukaemia with normal cytogenetics.Br J Haematol. 2015 Aug;170(3):305-22. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13409. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25891481 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse Models of Frequently Mutated Genes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;13(24):6192. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246192. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Palbociclib in Acute Leukemias With KMT2A-rearrangement: Results of AMLSG 23-14 Trial.Hemasphere. 2023 Apr 21;7(5):e877. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000877. eCollection 2023 May. Hemasphere. 2023. PMID: 37101762 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Combination of menin and kinase inhibitors as an effective treatment for leukemia with NUP98 translocations.Leukemia. 2024 Aug;38(8):1674-1687. doi: 10.1038/s41375-024-02312-9. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Leukemia. 2024. PMID: 38890447 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment for Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Hemasphere. 2021 Jun 1;5(6):e572. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000572. eCollection 2021 Jun. Hemasphere. 2021. PMID: 34095756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Menin in Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;15(9):1231. doi: 10.3390/genes15091231. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336822 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

