An Activity-Mediated Transition in Transcription in Early Postnatal Neurons
- PMID: 32589877
- PMCID: PMC7486250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.008
An Activity-Mediated Transition in Transcription in Early Postnatal Neurons
Abstract
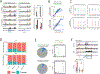
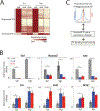
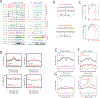
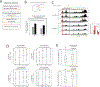
The maturation of the mammalian brain occurs after birth, and this stage of neuronal development is frequently impaired in neurological disorders, such as autism and schizophrenia. However, the mechanisms that regulate postnatal brain maturation are poorly defined. By purifying neuronal subpopulations across brain development in mice, we identify a postnatal switch in the transcriptional regulatory circuits that operates in the maturing mammalian brain. We show that this developmental transition includes the formation of hundreds of cell-type-specific neuronal enhancers that appear to be modulated by neuronal activity. Once selected, these enhancers are active throughout adulthood, suggesting that their formation in early life shapes neuronal identity and regulates mature brain function.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
'Enhancing' brain maturation.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020 Sep;21(9):450-451. doi: 10.1038/s41583-020-0352-9. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32678311 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

