A Fast and Accurate Method for Genome-Wide Time-to-Event Data Analysis and Its Application to UK Biobank
- PMID: 32589924
- PMCID: PMC7413891
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2020.06.003
A Fast and Accurate Method for Genome-Wide Time-to-Event Data Analysis and Its Application to UK Biobank
Abstract
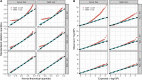
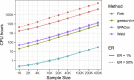
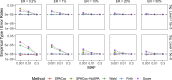
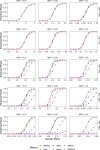
With increasing biobanking efforts connecting electronic health records and national registries to germline genetics, the time-to-event data analysis has attracted increasing attention in the genetics studies of human diseases. In time-to-event data analysis, the Cox proportional hazards (PH) regression model is one of the most used approaches. However, existing methods and tools are not scalable when analyzing a large biobank with hundreds of thousands of samples and endpoints, and they are not accurate when testing low-frequency and rare variants. Here, we propose a scalable and accurate method, SPACox (a saddlepoint approximation implementation based on the Cox PH regression model), that is applicable for genome-wide scale time-to-event data analysis. SPACox requires fitting a Cox PH regression model only once across the genome-wide analysis and then uses a saddlepoint approximation (SPA) to calibrate the test statistics. Simulation studies show that SPACox is 76-252 times faster than other existing alternatives, such as gwasurvivr, 185-511 times faster than the standard Wald test, and more than 6,000 times faster than the Firth correction and can control type I error rates at the genome-wide significance level regardless of minor allele frequencies. Through the analysis of UK Biobank inpatient data of 282,871 white British European ancestry samples, we show that SPACox can efficiently analyze large sample sizes and accurately control type I error rates. We identified 611 loci associated with time-to-event phenotypes of 12 common diseases, of which 38 loci would be missed within a logistic regression framework with a binary phenotype defined as event occurrence status during the follow-up period.
Keywords: Cox proportional hazards regression model; GWAS; PheWAS; UK Biobank; electronic health record; saddlepoint approximation; survival analysis; time-to-event data.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Fast and Accurate Method for Genome-wide Scale Phenome-wide G × E Analysis and Its Application to UK Biobank.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Dec 5;105(6):1182-1192. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 31735295 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies.Nat Genet. 2018 Sep;50(9):1335-1341. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0184-y. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 30104761 Free PMC article.
-
UK Biobank Whole-Exome Sequence Binary Phenome Analysis with Robust Region-Based Rare-Variant Test.Am J Hum Genet. 2020 Jan 2;106(1):3-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.11.012. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Am J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31866045 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable and Robust Regression Methods for Phenome-Wide Association Analysis on Large-Scale Biobank Data.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 15;12:682638. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.682638. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34211504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The UK Biobank: A Shining Example of Genome-Wide Association Study Science with the Power to Detect the Murky Complications of Real-World Epidemiology.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2022 Aug 31;23:569-589. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genom-121321-093606. Epub 2022 May 4. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2022. PMID: 35508184 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide association study reveals BET1L associated with survival time in the 137,693 Japanese individuals.Commun Biol. 2023 Feb 3;6(1):143. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04491-0. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 36737517 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the protective role of maternal lung cancer history on allergic rhinitis.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2025 Mar;76(2):156-163. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.24-172. Epub 2024 Dec 27. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40151401 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association studies using disease liabilities from deep neural networks.Am J Hum Genet. 2025 Mar 6;112(3):675-692. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2025.01.019. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2025. PMID: 39986278 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide analysis of 340 318 participants identifies four novel loci associated with the age of first spectacle wear.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Aug 25;31(17):3012-3019. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac048. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 35220419 Free PMC article.
-
Testing microbiome associations with survival times at both the community and individual taxon levels.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Sep 14;18(9):e1010509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010509. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36103548 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

