PKCλ/ι Loss Induces Autophagy, Oxidative Phosphorylation, and NRF2 to Promote Liver Cancer Progression
- PMID: 32589943
- PMCID: PMC7423690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.05.018
PKCλ/ι Loss Induces Autophagy, Oxidative Phosphorylation, and NRF2 to Promote Liver Cancer Progression
Abstract
Oxidative stress plays a critical role in liver tissue damage and in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) initiation and progression. However, the mechanisms that regulate autophagy and metabolic reprogramming during reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and how ROS promote tumorigenesis, still need to be fully understood. We show that protein kinase C (PKC) λ/ι loss in hepatocytes promotes autophagy and oxidative phosphorylation. This results in ROS generation, which through NRF2 drives HCC through cell-autonomous and non-autonomous mechanisms. Although PKCλ/ι promotes tumorigenesis in oncogene-driven cancer models, emerging evidence demonstrate that it is a tumor suppressor in more complex carcinogenic processes. Consistently, PKCλ/ι levels negatively correlate with HCC histological tumor grade, establishing this kinase as a tumor suppressor in liver cancer.
Keywords: NRF2; PKCζ; PKCι; PKCλ; atypical PKC; autophagy; hepatocellular carcinoma; metabolic reprogramming; oxidative phosphorylation; reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
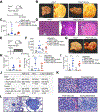
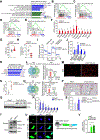


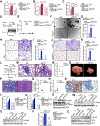
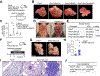
Comment in
-
The interplay between PRKCI/PKCλ/ι, SQSTM1/p62, and autophagy orchestrates the oxidative metabolic response that drives liver cancer.Autophagy. 2020 Oct;16(10):1915-1917. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1797290. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 32686580 Free PMC article.
-
PKCλ/ι Loss Induces Metabolic Reprogramming in Liver Cancer: Hitting Two Birds with One Stone?Cancer Cell. 2020 Aug 10;38(2):152-154. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.07.003. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32781040
References
-
- Duran A, Hernandez ED, Reina-Campos M, Castilla EA, Subramaniam S, Raghunandan S, Roberts LR, Kisseleva T, Karin M, Diaz-Meco MT, and Moscat J (2016). p62/SQSTM1 by Binding to Vitamin D Receptor Inhibits Hepatic Stellate Cell Activity, Fibrosis, and Liver Cancer. Cancer Cell 30, 595–609. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duran A, Linares JF, Galvez AS, Wikenheiser K, Flores JM, Diaz-Meco MT, and Moscat J (2008). The Signaling Adaptor p62 Is an Important NF-[kappa]B Mediator in Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 13, 343–354. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB (2011). Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 365, 1118–1127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

