Adenosine/A2B Receptor Signaling Ameliorates the Effects of Aging and Counteracts Obesity
- PMID: 32589947
- PMCID: PMC7437516
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.006
Adenosine/A2B Receptor Signaling Ameliorates the Effects of Aging and Counteracts Obesity
Erratum in
-
Adenosine/A2B Receptor Signaling Ameliorates the Effects of Aging and Counteracts Obesity.Cell Metab. 2022 Apr 5;34(4):649. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.02.014. Cell Metab. 2022. PMID: 35385706 No abstract available.
Abstract
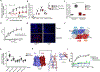
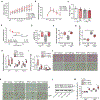
The combination of aging populations with the obesity pandemic results in an alarming rise in non-communicable diseases. Here, we show that the enigmatic adenosine A2B receptor (A2B) is abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle (SKM) as well as brown adipose tissue (BAT) and might be targeted to counteract age-related muscle atrophy (sarcopenia) as well as obesity. Mice with SKM-specific deletion of A2B exhibited sarcopenia, diminished muscle strength, and reduced energy expenditure (EE), whereas pharmacological A2B activation counteracted these processes. Adipose tissue-specific ablation of A2B exacerbated age-related processes and reduced BAT EE, whereas A2B stimulation ameliorated obesity. In humans, A2B expression correlated with EE in SKM, BAT activity, and abundance of thermogenic adipocytes in white fat. Moreover, A2B agonist treatment increased EE from human adipocytes, myocytes, and muscle explants. Mechanistically, A2B forms heterodimers required for adenosine signaling. Overall, adenosine/A2B signaling links muscle and BAT and has both anti-aging and anti-obesity potential.
Keywords: GPCR; adenosine; adenosine receptor A2B; aging; brown adipose tissue; browning; energy metabolism; muscle; obesity; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests T.G., L.R.-S., F.C., D.W., J.N., A.H., S.H.-B., B.K.F., and A.P. have filed an application for patenting A2B agonist treatment of musculoskeletal disorders.
Figures


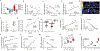
Comment in
-
Age-related muscle loss - novel target identified.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020 Sep;16(9):472-473. doi: 10.1038/s41574-020-0388-y. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32636472 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barbat-Artigas S, Rolland Y, Zamboni M, and Aubertin-Leheudre M (2012). How to assess functional status: a new muscle quality index. The journal of nutrition, health & aging 16, 67–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

