Community-acquired pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Chinese adult: A case report
- PMID: 32590802
- PMCID: PMC7329007
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020914
Community-acquired pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a Chinese adult: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has been established as an important cause of severe community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) with very high mortality. Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) producing MRSA has been reported to be associated with necrotizing pneumonia and worse outcome. The incidence of community-acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA) pneumonia is very low, as only a few CA-MRSA pneumonia cases were reported in the last few years. We present a case of severe CAP caused by PVL-positive MRSA with ensuing septic shock.
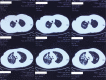
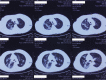
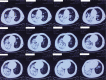
Patient concerns: A 68-year-old male with no concerning medical history had developed a fever that reached 39.0°C, a productive cough that was sustained for 5 days, and hypodynamia. He was treated with azithromycin and alexipyretic in a nearby clinic for 2 days in which the symptoms were alleviated. However, 1 day later, the symptoms worsened, and he was taken to a local Chinese medicine hospital for traditional medicine treatment. However, his clinical condition deteriorated rapidly, and he then developed dyspnea and hemoptysis.
Diagnosis: CA-MRSA pneumonia and septic shock. The sputum culture showed MRSA. Polymerase chain reaction of MRSA isolates was positive for PVL genes.
Interventions: Mechanical ventilation, fluid resuscitation, and antibiotic therapy were performed. Antibiotic therapy included mezlocillin sodium/sulbactam sodium, linezolid, and oseltamivir.
Outcomes: He died after 12 hours of treatment.
Lessons: This is a report of severe pneumonia due to PVL-positive CA-MRSA in a healthy adult. CA-MRSA should be considered a pathogen of severe CAP, especially when combined with septic shock in previously healthy individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Vardakas KZ, Matthaiou DK, Falagas ME. Incidence, characteristics and outcomes of patients with severe community acquired-MRSA pneumonia. Eur Respir J 2009;34:1148–58. - PubMed
-
- Aliberti S, Reyes LF, Faverio P, et al. Global initiative for meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia (GLIMP): an international, observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis 2016;16:1364–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous