Could there be a link between oral hygiene and the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections?
- PMID: 32591714
- PMCID: PMC7319209
- DOI: 10.1038/s41415-020-1747-8
Could there be a link between oral hygiene and the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections?
Abstract
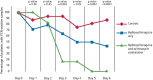
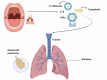
On 30 January 2020, the World Health Organisation identified COVID-19, caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, to be a global emergency. The risk factors already identified for developing complications from a COVID-19 infection are age, gender and comorbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity and cardiovascular disease. These risk factors, however, do not account for the other 52% of deaths arising from COVID-19 in often seemingly healthy individuals. This paper investigates the potential link between SARS-CoV-2 and bacterial load, questioning whether bacteria may play a role in bacterial superinfections and complications such as pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome and sepsis. The connection between COVID-19 complications and oral health and periodontal disease is also examined, as the comorbidities at highest risk of COVID-19 complications also cause imbalances in the oral microbiome and increase the risk of periodontal disease. We explore the connection between high bacterial load in the mouth and post-viral complications, and how improving oral health may reduce the risk of complications from COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the study.
Figures
Comment in
-
Scientific rigour.Br Dent J. 2020 Nov;229(9):569-570. doi: 10.1038/s41415-020-2362-4. Br Dent J. 2020. PMID: 33188313 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lingonberry polyphenols: Potential SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors as nutraceutical tools?Physiol Rep. 2021 Feb;9(3):e14741. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14741. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33527774 Free PMC article.
Comment on
-
A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019.N Engl J Med. 2020 Feb 20;382(8):727-733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. Epub 2020 Jan 24. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 31978945 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Clinical Management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infection is suspected. 2020. Available online at https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330893 (accessed June 2020).
-
- World Health Organisation. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. 2020. Available online at https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed June 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

