Biochemical determinants of the IGFBP-3-hyaluronan interaction
- PMID: 32592613
- PMCID: PMC7396449
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.12919
Biochemical determinants of the IGFBP-3-hyaluronan interaction
Abstract
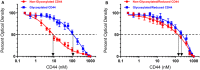
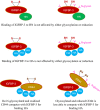
IGFBP-3, the most abundant IGFBP and the main carrier of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in the circulation, can bind IGF-1 with high affinity, which attenuates IGF/IGF-IR interactions, thereby resulting in antiproliferative effects. The C-terminal domain of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) is known to contain an 18-basic amino acid motif capable of interacting with either humanin (HN) or hyaluronan (HA). We previously showed that the 18-amino acid IGFBP-3 peptide is capable of binding either HA or HN with comparable affinities to the full-length IGFBP-3 protein and that IGFBP-3 can compete with the HA receptor, CD44, for binding HA. Blocking the interaction between HA and CD44 reduced viability of A549 human lung cancer cells. In this study, we set out to better characterize IGFBP-3-HA interactions. We show that both stereochemistry and amino acid identity are important determinants of the interaction between the IGFBP-3 peptide and HA and for the peptide's ability to exert its cytotoxic effects. Binding of IGFBP-3 to either HA or HN was unaffected by glycosylation or reduction of IGFBP-3, suggesting that the basic 18-amino acid residue sequence of IGFBP-3 remains accessible for interaction with either HN or HA upon glycosylation or reduction of the full-length protein. Removing N-linked oligosaccharides from CD44 increased its ability to compete with IGFBP-3 for binding HA, while reduction of CD44 rendered the protein relatively ineffective at blocking IGFBP-3-HA interactions. We conclude that both deglycosylation and disulfide bond formation are important for CD44 to compete with IGFBP-3 for binding HA.
Keywords: CD44; IGFBP-3; humanin; hyaluronan; kinetics; peptide.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors read and approved the final manuscript and declare no conflict of interest with the contents of this article. ‘The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health’.
Figures
References
-
- Firth SM and Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin‐like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23, 824–854. - PubMed
-
- Baxter RC (2014) IGF binding proteins in cancer: mechanistic and clinical insights. Nat Rev Cancer 14, 329–341. - PubMed
-
- Butt AJ and Williams AC (2001) IGFBP‐3 and apoptosis—a licence to kill? Apoptosis 6, 199–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

