Suboptimal Biological Sampling as a Probable Cause of False-Negative COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Results
- PMID: 32594170
- PMCID: PMC7337811
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa370
Suboptimal Biological Sampling as a Probable Cause of False-Negative COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Results
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Suboptimal Biological Sampling as a Probable Cause of False-Negative COVID-19 Diagnostic Test Results.J Infect Dis. 2021 Jul 2;224(1):184. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab230. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34057182 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
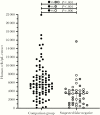
False-negative severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 test results can negatively impact the clinical and public health response to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We used droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (ddPCR) to demonstrate that human DNA levels, a stable molecular marker of sampling quality, were significantly lower in samples from 40 confirmed or suspected COVID-19 cases that yielded negative diagnostic test results (ie, suspected false-negative test results) compared with a representative pool of 87 specimens submitted for COVID-19 testing. Our results support suboptimal biological sampling as a contributor to false-negative COVID-19 test results and underscore the importance of proper training and technique in the collection of nasopharyngeal specimens.
Keywords: COVID-19; ddPCR; false negative; nasopharyngeal swab; sample quality.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens from Persons for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). 2020. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/guidelines-clinical-specim.... Accessed 23 March 2020.
-
- Prinzi A. False Negatives and Reinfections: the Challenges of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Testing Available at: https://asm.org/Articles/2020/April/False-Negatives-and-Reinfections-the.... Accessed 3 May 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

