Development and Stability Study of an Omeprazole Suppository for Infants
- PMID: 32594306
- PMCID: PMC7511457
- DOI: 10.1007/s13318-020-00629-1
Development and Stability Study of an Omeprazole Suppository for Infants
Abstract
Background and objective: Omeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that is used in acid suppression therapy in infants. In this study we aimed to develop a pediatric omeprazole suppository, with good physical and chemical stability, suitable for pharmaceutical batch production.
Methods: The composition of the suppository consisted of omeprazole, witepsol H15 and arginine (L) base. To achieve evenly distributed omeprazole suspension suppositories, the temperature, stirring rate, and arginine (L) base amount were varied. A previously validated quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet method was modified and a long-term stability study was performed for one year.
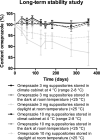
Results: Evenly distributed omeprazole suspension suppositories were obtained by adding 100 mg arginine (L) base and pouring at a temperature of 34.7 °C and a stirring speed of 200 rpm. The long-term stability study showed no signs of discoloration and a stable omeprazole content between 90 and 110% over 1 year if stored in the dark at room temperature.
Conclusion: We developed a pediatric omeprazole suppository. This formulation may provide a good alternative to manipulated commercial or extemporaneously compounded omeprazole oral formulations for infants. Clinical studies are needed to establish efficacy and safety in this young population.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization of the manufacturing process of a pediatric omeprazole enteric pellets suspension: Full Factorial Design.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2025 May;51(5):397-408. doi: 10.1080/03639045.2025.2476651. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40047104
-
Stability of partial doses of omeprazole-sodium bicarbonate oral suspension.Ann Pharmacother. 2007 Dec;41(12):1954-61. doi: 10.1345/aph.1K246. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Ann Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17956960
-
Stability and viscosity of a flavored omeprazole oral suspension for pediatric use.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006 Nov 15;63(22):2240-7. doi: 10.2146/ajhp060026. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006. PMID: 17090745
-
[Pharmacy compounding of an omeprazole suspension].J Pharm Belg. 2009 Jun;(2):54-63. J Pharm Belg. 2009. PMID: 19739529 Review. French.
-
Comparison of 24-hour intragastric pH using four liquid formulations of lansoprazole and omeprazole.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1999 Dec 1;56(23 Suppl 4):S18-21. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/56.suppl_4.S18. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1999. PMID: 10597120 Review.
Cited by
-
Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole Alters the Spiking Characteristics of Proteinoids.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 27;10(5):5016-5035. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10790. eCollection 2025 Feb 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39959035 Free PMC article.
-
Nurses' knowledge and practice regarding mixing medications with food: a multicenter cross-sectional study from a developing country.J Health Popul Nutr. 2023 Jun 5;42(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s41043-023-00396-0. J Health Popul Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37277885 Free PMC article.
-
Rectal Omeprazole in Infants With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Randomized Pilot Trial.Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020 Oct;45(5):635-643. doi: 10.1007/s13318-020-00630-8. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2020. PMID: 32594305 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Formulation of Dosage Forms with Proton Pump Inhibitors: State of the Art, Challenges and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 25;14(10):2043. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102043. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Galenic Strategies for Developing Gastro-Resistant Omeprazole Formulation for Pediatrics.Children (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;11(8):945. doi: 10.3390/children11080945. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39201880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosen R, Vandenplas Y, Singendonk M, Cabana M, Dilorenzo C, Gottrand F, et al. Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Clinical Practice Guidelines: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J Pediatric Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;66:516–554. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001889. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources