SAFETY AND EFFECTS OF CRATAEGUS EXTRACT WS 1442 AND NORDIC WALKING ON LIPID PROFILE AND ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION: A RANDOMIZED, PARTIALLY BLINDED PILOT STUDY IN OVERWEIGHT VOLUNTEERS
- PMID: 32595244
- PMCID: PMC7314302
- DOI: 10.20471/acc.2019.58.04.06
SAFETY AND EFFECTS OF CRATAEGUS EXTRACT WS 1442 AND NORDIC WALKING ON LIPID PROFILE AND ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION: A RANDOMIZED, PARTIALLY BLINDED PILOT STUDY IN OVERWEIGHT VOLUNTEERS
Abstract
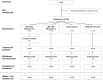
Overweight and physical inactivity adversely affect endothelial function and are risk factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Both Crataegus extract WS 1442 and physical exercise exert beneficial effects on endothelial function. We investigated whether WS 1442 and Nordic walking (NW) had comparable effects on endothelial function and lipid profile in overweight subjects. In this partially blinded pilot study, overweight, otherwise healthy volunteers aged 45-75 years were randomized into four groups as follows: WS 1442 2x450 mg/day (WS-standard), WS 1442 2x900 mg/day (WS-double), exercise 2x30 minutes/week (NW-low), and exercise 4x45 minutes/week (NW-high) for 12 weeks. Safety was assessed based on adverse events. Endothelial function testing (EndoPAT®), assessment of endothelial progenitor cells, lipid profiles, and treadmill testing were performed. Sixty subjects participated in the study. At baseline, subjects in WS-standard/-double groups had higher lipid levels and greater impairment of endothelial function. Subjects with impaired endothelial function showed improvement regardless of the type of intervention. Subjects in WS-standard and WS-double groups showed a trend towards modest decrease in triglycerides and modest increase in HDL-cholesterol; most changes were within the normal limits. In NW-low/-high groups, values also remained within the normal range. Exercise capacity improved in both NW groups. WS-double showed no additional benefits over WS-standard. All adverse events were unrelated or improbably related to treatment. In conclusion, WS 1442 and exercise training were safe and showed beneficial effects on endothelial function and lipid profile in overweight but otherwise healthy volunteers; exercise capacity improved only by Nordic walking.
Keywords: Crataegus extract WS 1442; Endothelial progenitor cells; Exercise; Overweight.
Figures
References
-
- Busse WR, Juretzek W, Koch E. Hawthorn (Crataegus). In: Coates P, Blackman MR, Cragg G, Levine M, Moss J, White J, editors. Encylopedia of Dietary Supplements. New York: Marcel Dekker, 2005; p. 337-47.
-
- Anselm E, Socorro VF, Dal-Ros S, Schott C, Bronner C, Schini-Kerth VB. Crataegus special extract WS 1442 causes endothelium-dependent relaxation via a redox-sensitive Src- and Akt-dependent activation of endothelial NO synthase but not via activation of estrogen receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009;53(3):253–60. 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31819ccfc9 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
