Covid-19: current knowledge, disease potential, prevention and clinical advances
- PMID: 32595349
- PMCID: PMC7314501
- DOI: 10.3906/biy-2005-29
Covid-19: current knowledge, disease potential, prevention and clinical advances
Abstract
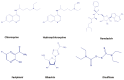
The top priority of any nation is to lead the nation towards prosperity, progress, and economic growth, confronting several challenges and concerns arisen from global situations. The sudden outbreak of any disease defies the health care systems and economy of nations. COVID-19 is one of the viral diseases which broke out in Wuhan city of China in 2019. COVID-19 outbreak intermittently prevailed all over the world. It exposes the fragility of the established health care systems across the world in spite of comprising modern science and technology. Unfortunately, there is no chemotherapeutic agent in the regimen of antiviral drugs or no vaccine available to curb this infectious disease. As a consequence, this deadly infection has prevailed all over the world. The antiviral drugs used for viral diseases excluding COVID-19 infection are Ramdesvir, Favipiravir, and Ribavarin, and antimalarial agents (Chloroquine & Hydroxychloroquine) are being administered to the patients for redemption of this infection. Fortunately, these existing drugs have been found clinically active and are being used. In this review, we present the current scenario and status of epidemiology, diagnosis, treatment, vaccine development for COVID-19, and its impact on the socio-economic structure.
Keywords: COVID-19; antivirals; financial crisis; mortality rate; transmission rate (Ro); vaccines.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alam A Imam N Farooqui A Ali S Malik Md Recent trends in ZikV research: A step away from cure. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2017;91:1152. - PubMed
-
- Chhikara BS Rathi B Singh J Poonam Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 disease COVID-19: Infection, prevention and clinical advances of the prospective chemical drug therapeutics. Chemical Biology Letters. 2020;7:63.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials