Phylogenetic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes in Turkey
- PMID: 32595351
- PMCID: PMC7314511
- DOI: 10.3906/biy-2005-35
Phylogenetic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes in Turkey
Abstract
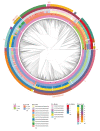
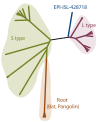
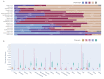
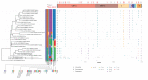
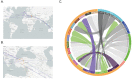
COVID-19 has effectively spread worldwide. As of May 2020, Turkey is among the top ten countries with the most cases. A comprehensive genomic characterization of the virus isolates in Turkey is yet to be carried out. Here, we built a phylogenetic tree with globally obtained 15,277 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) genomes. We identified the subtypes based on the phylogenetic clustering in comparison with the previously annotated classifications. We performed a phylogenetic analysis of the first 30 SARS-CoV-2 genomes isolated and sequenced in Turkey. We suggest that the first introduction of the virus to the country is earlier than the first reported case of infection. Virus genomes isolated from Turkey are dispersed among most types in the phylogenetic tree. We find 2 of the seventeen subclusters enriched with the isolates of Turkey, which likely have spread expansively in the country. Finally, we traced virus genomes based on their phylogenetic placements. This analysis suggested multiple independent international introductions of the virus and revealed a hub for the inland transmission. We released a web application to track the global and interprovincial virus spread of the isolates from Turkey in comparison to thousands of genomes worldwide.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; evolution; genome sequence; phylogenetics.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: none declared
Figures
References
-
- Bhattacharyya C Das C Ghosh A Singh AK Mukherjee S Global spread of SARS-CoV-2 subtype with spike protein mutation D614G is shaped by human genomic variations that regulate expression of TMPRSS2 and MX1 genes. BioRxiv. 2020;10
-
- Dos Ramos F Carrasco M Doyle T Brierley I Programmed -1 ribosomal frameshifting in the SARS coronavirus. Biochemical Society Transactions. 2004;32:1081. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
