Precise CRISPR-Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing in Super Basmati Rice for Resistance Against Bacterial Blight by Targeting the Major Susceptibility Gene
- PMID: 32595655
- PMCID: PMC7304078
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00575
Precise CRISPR-Cas9 Mediated Genome Editing in Super Basmati Rice for Resistance Against Bacterial Blight by Targeting the Major Susceptibility Gene
Abstract
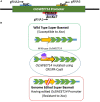
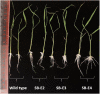
Basmati rice is famous around the world for its flavor, aroma, and long grain. Its demand is increasing worldwide, especially in Asia. However, its production is threatened by various problems faced in the fields, resulting in major crop losses. One of the major problems is bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Xoo hijacks the host machinery by activating the susceptibility genes (OsSWEET family genes), using its endogenous transcription activator like effectors (TALEs). TALEs have effector binding elements (EBEs) in the promoter region of the OsSWEET genes. Out of six well-known TALEs found to have EBEs in Clade III SWEET genes, four are present in OsSWEET14 gene's promoter region. Thus, targeting the promoter of OsSWEET14 is very important for creating broad-spectrum resistance. To engineer resistance against bacterial blight, we established CRISPR-Cas9 mediated genome editing in Super Basmati rice by targeting 4 EBEs present in the promoter of OsSWEET14. We were able to obtain four different Super Basmati lines (SB-E1, SB-E2, SB-E3, and SB-E4) having edited EBEs of three TALEs (AvrXa7, PthXo3, and TalF). The edited lines were then evaluated in triplicate for resistance against bacterial blight by choosing one of the locally isolated virulent Xoo strains with AvrXa7 and infecting Super Basmati. The lines with deletions in EBE of AvrXa7 showed resistance against the Xoo strain. Thus, it was confirmed that edited EBEs provide resistance against their respective TALEs present in Xoo strains. In this study up to 9% editing efficiency was obtained. Our findings showed that CRISPR-Cas9 can be harnessed to generate resistance against bacterial blight in indigenous varieties, against locally prevalent Xoo strains.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; Xanthomonas oryzae; bacterial blight; genome editing; rice improvement.
Copyright © 2020 Zafar, Khan, Amin, Mukhtar, Yasmin, Arif, Ejaz and Mansoor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Engineering Broad-Spectrum Bacterial Blight Resistance by Simultaneously Disrupting Variable TALE-Binding Elements of Multiple Susceptibility Genes in Rice.Mol Plant. 2019 Nov 4;12(11):1434-1446. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2019.08.006. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Mol Plant. 2019. PMID: 31493565
-
The Rice ILI2 Locus Is a Bidirectional Target of the African Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Major Transcription Activator-like Effector TalC but Does Not Contribute to Disease Susceptibility.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 16;23(10):5559. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105559. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628368 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted promoter editing for rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae reveals differential activities for SWEET14-inducing TAL effectors.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Mar;15(3):306-317. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12613. Epub 2016 Dec 17. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 27539813 Free PMC article.
-
Deployment of Genetic and Genomic Tools Toward Gaining a Better Understanding of Rice-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Interactions for Development of Durable Bacterial Blight Resistant Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 4;11:1152. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01152. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32849710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance Genes and their Interactions with Bacterial Blight/Leaf Streak Pathogens (Xanthomonas oryzae) in Rice (Oryza sativa L.)-an Updated Review.Rice (N Y). 2020 Jan 8;13(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y. Rice (N Y). 2020. PMID: 31915945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of SWEET Sugar Transporters in Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Responses.Cells. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):1303. doi: 10.3390/cells11081303. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35455982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of approaches to control bacterial leaf blight in rice.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 May 17;38(7):113. doi: 10.1007/s11274-022-03298-1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35578069 Review.
-
Advancements in Plant Gene Editing Technology: From Construct Design to Enhanced Transformation Efficiency.Biotechnol J. 2024 Dec;19(12):e202400457. doi: 10.1002/biot.202400457. Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39692063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Insights into Rice Immunity: Unveiling Mechanisms and Innovative Approaches to Combat Major Pathogens.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jun 1;14(11):1694. doi: 10.3390/plants14111694. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of CRISPR Technology in Gene Editing for Tolerance to Biotic Factors in Plants: A Systematic Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Oct 2;46(10):11086-11123. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100659. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451539 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

