Metformin Restores Tetracyclines Susceptibility against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
- PMID: 32596101
- PMCID: PMC7312304
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201902227
Metformin Restores Tetracyclines Susceptibility against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
Abstract
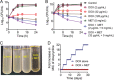
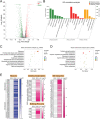
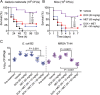
Highly persistent incidence of multidrug resistant (MDR) bacterial pathogens constitutes a global burden for public health. An alternative strategy to alleviate such a crisis is to identify promising compounds to restore antibiotics activity against MDR bacteria. It is reported that the antidiabetic drug metformin exhibits the potentiation effect on tetracycline antibiotics, particularly doxycycline and minocycline, against MDR S. aureus, E. faecalis, E. coli, and S. enteritidis. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that metformin promotes intracellular accumulation of doxycycline in tetracycline-resistant E. coli. In addition, metformin boosts the immune response and alleviates the inflammatory responses in vitro. Last, metformin fully restores the activity of doxycycline in three animal infection models. Collectively, these results reveal the potential of metformin as a novel tetracyclines adjuvant to circumvent MDR bacterial pathogens and to improve the treatment outcome of recalcitrant infections.
Keywords: antibiotic adjuvant; metformin; multidrug resistant bacteria; tetracycline.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by WILEY‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Yelin I., Kishony R., Cell 2018, 172, 1136. - PubMed
-
- Walsh T. R., Weeks J., Livermore D. M., Toleman M. A., Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 355. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y.‐Y., Wang Y., Walsh T. R., Yi L.‐X., Zhang R., Spencer J., Doi Y., Tian G., Dong B., Huang X., Yu L., Gu D., Ren H., Chen X., Lv L., He D., Zhou H., Liang Z., Liu J., Shen J., Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161. - PubMed
-
- He T., Wang R., Liu D., Walsh T. R., Zhang R., Lv Y., Ke Y., Ji Q., Wei R., Liu Z., Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1450. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
